Page 59 - GTM-1-2
P. 59
Global Translational Medicine A Taxonomy of AI Assisted Medical Robots
A B
C D
[76]
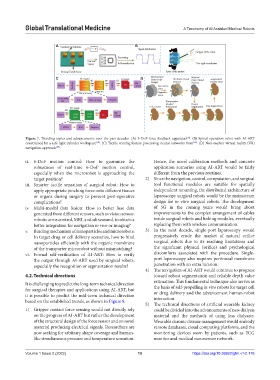
Figure 7. Trending topics and advancements over the past decades. (A) 3-DoF force feedback apparatus . (B) Spinal operation robot with AI-ART
[78]
[50]
constrained by a safe light cylinder workspace . (C) Tactile sensing feature processing neural networks from . (D) Non-marker virtual reality (VR)
navigation approach .
[57]
ii. 6-DoF motion control: How to guarantee the Hence, the novel calibration methods and concrete
robustness of real-time 6-DoF motion control, application scenarios using AI-ART would be fairly
especially when the microrobot is approaching the different from the previous routines.
target position? 2) Since the navigation, control, computation, and surgical
iii. Smarter tactile sensation of surgical robot: How to tool functional modules are suitable for spatially
apply appropriate pinching force onto different tissues independent mounting, the distributed architecture of
or organs during surgery to prevent post-operative laparoscopy surgical robots would be the mainstream
complications? design for in vitro surgical robots. The development
iv. Multi-modal data fusion: How to better fuse data of 5G in the coming years would bring about
generated from different sensors, such as vision sensor, improvements to the complex arrangement of cables
robotic arms control, MRI, and ultrasound, to obtain a inside surgical robots and linking modules, eventually
better integration for navigation in vivo or imaging? replacing them with wireless communication.
v. Binding mechanism of nanoparticles and microrobots: 3) In the next decade, single-port laparoscopy would
In target drug or cell delivery scenarios, how to bind progressively erode the market of natural orifice
nanoparticles efficiently with the organic membrane surgical robots due to its reaching limitations and
of the transporter microrobot without mismatching? the significant physical (orifice) and psychological
vi. Formal self-verification of AI-ART: How to verify discomforts associated with the procedure. Single-
the output through AI-ART used by surgical robots, port laparoscopy also requires peritoneal membrane
especially the recognition or segmentation results? penetration with an extra incision.
4) The navigation of AI-ART would continue to progress
4.2. Technical directions toward robust segmentation and reliable depth value
estimation. This fundamental technique also serves as
It is challenging to predict the long-term technical direction
for surgical therapies and applications using AI-ART, but the basis of self-propelling in vivo robots for target cell
it is possible to predict the mid-term technical direction or drug delivery and the advancement human-robot
based on the established trends, as shown in Figure 8. interaction.
5) The technical directions of artificial wearable kidney
1) Gripper contact force sensing would not directly rely could be divided into the advancements of new dialysis
on the progress of AI-ART but rather the development material and the methods of using less dialysate.
of the structural design of the force sensor and on novel Wearable chronic disease management would embody
material producing electrical signals. Researchers are remote databases, cloud computing platforms, and the
now seeking for arbitrary shape coverage and human- monitoring devices worn by patients, such as ECG
like simultaneous pressure and temperature sensation. monitor and medical nanosensor network.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.176