Page 60 - GTM-1-2
P. 60
Global Translational Medicine A Taxonomy of AI Assisted Medical Robots
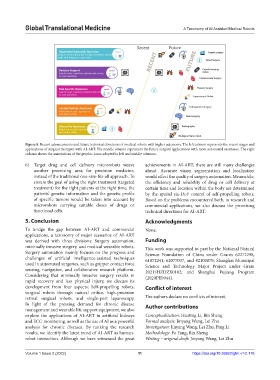
Figure 8. Recent advancements and future technical directions of medical robots with higher autonomy. The left column represents the recent stages and
applications of surgical therapies with AI-ART. The middle column represents the future surgical applications with more automated assistance. The right
column shows the annotations of the graphic icons adopted in left and middle columns.
6) Target drug and cell delivery microrobots weave achievements in AI-ART, there are still many challenges
another promising area for precision medicine, ahead. Accurate vision segmentation and localization
instead of the traditional one-size-fits-all approach. To would affect the quality of surgery automation. Meanwhile,
ensure the goal of using the right treatment (targeted the efficiency and reliability of drug or cell delivery at
treatment) for the right patients at the right time, the certain time and location within the body are determined
patients’ genetic information and the genetic profile by the spatial six-DoF control of self-propelling robots.
of specific tumors would be taken into account by Based on the problems encountered both, in research and
microrobots carrying suitable doses of drugs or commercial applications, we also discuss the promising
functional cells. technical directions for AI-ART.
5. Conclusion Acknowledgments
To bridge the gap between AI-ART and commercial None.
applications, a taxonomy of major scenarios of AI-ART
was derived with three divisions: Surgery automation, Funding
minimally invasive surgery, and medical wearable robots. This work was supported in part by the National Natural
Surgery automation mainly focuses on the progress and Science Foundation of China under Grants 62272298,
challenges of artificial intelligence-assisted techniques 61872241, 62077037, and 82100879; Shanghai Municipal
used in automated surgeries, such as gripper contact force Science and Technology Major Project under Grant
sensing, navigation, and collaborative research platform. 2021SHZDZX0102; and Shanghai Pujiang Program
Considering that minimally invasive surgery results in (2020PJD044).
rapid recovery and less physical injury, we discuss its
development from four aspects: Self-propelling robots, Conflict of interest
surgical robots through natural orifice, high-precision
retinal surgical robots, and single-port laparoscopy. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
In light of the pressing demand for chronic disease Author contributions
management and wearable life support equipment, we also
explore the applications of AI-ART in artificial kidneys Conceptualization: Huating Li, Bin Sheng
and ECG monitoring, as well as the use of AI as a powerful Formal analysis: Jinyang Wang, Lei Zhu
analysis for chronic diseases. By ranking the research Investigation: Jinyang Wang, Lei Zhu, Ping Li
results, we identify the latest trend of AI-ART as human- Methodology: Po Yang, Bin Sheng
robot interaction. Although we have witnessed the great Writing – original draft: Jinyang Wang, Lei Zhu
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.176