Page 67 - GTM-1-2
P. 67
Global Translational Medicineranslational Medicine
Global T Risk factors of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Risk factors of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
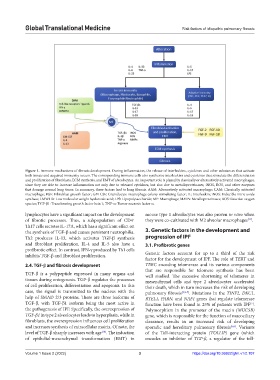
Figure 1. Immune mechanisms of fibrosis development. During inflammation, the release of interleukins, cytokines and other substances that activate
both innate and acquired immunity occurs. The corresponding immune cells also synthesize interleukins and cytokines that stimulate the differentiation
and proliferation of fibroblasts, ECM synthesis, and EMT of alveolocytes. An important role is played by classically or alternatively activated macrophages,
since they are able to increase inflammation not only due to released cytokines, but also due to metalloproteinases, iNOS, ROS, and other enzymes
that damage normal lung tissue. In summary, these factors lead to lung fibrosis. AAM: Alternatively activated macrophage; CAM: Classically activated
macrophage; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL: Interleukin; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide
synthase; LMWHA: Low molecular weight hyaluronic acid; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MF: Macrophage; MMPs: Metalloproteinases; ROS: Reactive oxygen
species; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta 1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α.
lymphocytes have a significant impact on the development mouse type 1 alveolocytes was also proven in vitro when
[11]
+
of fibrotic processes. Thus, a subpopulation of CD4 they were co-cultivated with M2 alveolar macrophages .
Th17 cells secretes IL-17A, which has a significant effect on
the synthesis of TGF-β and causes persistent neutrophilia. 3. Genetic factors in the development and
Th2 produces IL-13, which activates TGF-β synthesis progression of IPF
and fibroblast proliferation. IL-4 and IL-5 also have a 3.1. Profibrotic genes
profibrotic effect. In contrast, IFN-γ produced by Th1 cells
inhibits TGF-β and fibroblast proliferation. Genetic factors account for up to a third of the risk
factor for the development of IPF. The role of TERT and
2.4. TGF-β and fibrosis development TERC encoding telomerase and its various components
that are responsible for telomere synthesis has been
TGF-β is a polypeptide expressed in many organs and well studied. The excessive shortening of telomeres in
tissues during ontogenesis. TGF-β regulates the processes mesenchymal cells and type 2 alveolocytes accelerated
of cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. In this their death, which in turn increases the risk of developing
case, the signal is transmitted to the nucleus with the pulmonary fibrosis [1,5-7] . Mutations in the TINF2, DKC1,
help of SMAD 2/3 proteins. There are three isoforms of RTEL1, PARN, and NAF1 genes that regulate telomerase
TGF-β, with TGF-β1 isoform being the most active in function have been found in 25% of patients with IPF .
[7]
the pathogenesis of IPF. Specifically, the overexpression of Polymorphism in the promoter of the mucin (MUC5B)
TGF-β1 in type 2 alveolocytes leads to hyperplasia, while in gene, which is responsible for the function of mucociliary
fibroblasts, the overexpression influences cell proliferation clearance, results in an increased risk of developing
and increases synthesis of extracellular matrix. Of note, the sporadic and hereditary pulmonary fibrosis [5,6] . Variants
level of TGF-β sharply increases with age . The induction of the Toll-interacting protein (TOLLIP) gene (which
[10]
of epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) in encodes an inhibitor of TGF-β, a regulator of the toll-
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.107