Page 66 - GTM-2-3
P. 66
Global Translational Medicine Influence of ferroptosis in neurological diseases
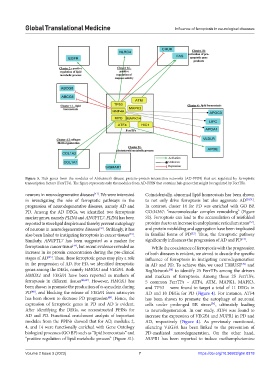
Figure 5. Hub genes from the modules of Alzheimer’s disease protein–protein interaction networks (AD-PPIN) that are regulated by ferroptotic
transcription factors (FerrTFs). The figure represents only the modules from AD-PPIN that contains hub genes that might be regulated by FerrTFs.
neurons in neurodegenerative diseases . We were interested Coincidentally, abnormal lipid homeostasis has been shown
[41]
in investigating the role of ferroptotic pathways in the to not only drive ferroptosis but also aggravate AD [50,51] .
progression of neurodegenerative diseases, namely AD and In contrast, cluster 14 for PD was enriched with GO BP,
PD. Among the AD DEGs, we identified two ferroptosis GO:34367: “macromolecular complex remodeling” (Figure
marker genes, namely PLIN4 and ANGPTL7. PLIN4 has been S2). Ferroptosis can lead to the accumulation of misfolded
[52]
reported to store lipid droplets and thereby prevent mitophagy proteins due to an increase in endoplasmic reticulum stress ,
of neurons in neurodegenerative diseases . Strikingly, it has and protein misfolding and aggregation have been implicated
[42]
[53]
also been linked to instigating ferroptosis in cancer tissues . in familial forms of PD . Thus, the ferroptotic pathway
[43]
[13]
Similarly, ANGPTL7 has been suggested as a marker for significantly influences the progression of AD and PD .
ferroptosis in cancer tissue , but recent evidence revealed an While the coexistence of ferroptosis with the progression
[44]
increase in its protein concentration during the pre-clinical of both diseases is evident, we aimed to decode the specific
[45]
stages of AD . Thus, these ferroptotic genes may play a role influence of ferroptosis in instigating neurodegeneration
in the progression of AD. For PD, we identified ferroptotic in AD and PD. To achieve this, we used TRRUST and
[29]
genes among the DEGs, namely HMOX1 and VEGFA. Both RegNetwork to identify 25 FerrTFs among the drivers
[30]
HMOX1 and VEGFA have been reported as markers of and markers of ferroptosis. Among these 25 FerrTFs,
ferroptosis in different tissues [46,47] . However, HMOX1 has 5 common FerrTFs – ATF4, ATM, MAPK1, MAPK3,
been shown to promote the production of α-synuclein during and TP53 – were found to target a total of 11 DEGs in
PD , and blocking the release of VEGFA from astrocytes AD and 10 DEGs for PD (Figure 4). For instance, ATF4
[48]
has been shown to decrease PD progression . Hence, the has been shown to promote the autophagy of neuronal
[49]
expression of ferroptotic genes in PD and AD is evident. cells under prolonged ER stress , ultimately leading
[54]
After identifying the DEGs, we reconstructed PPINs for to neurodegeneration. In our study, ATF4 was found to
AD and PD. Functional enrichment analysis of important increase the expression of VEGFA and NUPR1 in PD and
modules from the PPINs showed that for AD, modules 2, AD, respectively (Figure 4). As previously mentioned,
4, and 14 were functionally enriched with Gene Ontology silencing VEGFA has been linked to the prevention of
biological processes (GO BP) such as “lipid homeostasis” and PD-mediated neurodegeneration. On the other hand,
“positive regulation of lipid metabolic process” (Figure S1). NUPR1 has been reported to induce methamphetamine
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.0318