Page 62 - IJAMD-1-2
P. 62
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
AI-assisted ML monitoring in additive auxetics
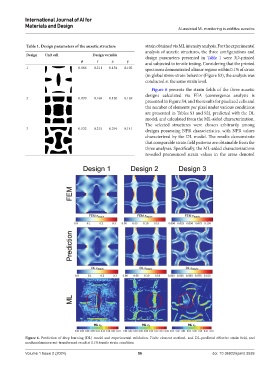
Table 1. Design parameters of the auxetic structure strain obtained via ML intensity analysis. For the experimental
analysis of auxetic structures, the three configurations and
Design Unit cell Design variable design parameters presented in Table 1 were 3D-printed
ϕ τ x y and subjected to tensile testing. Considering that the printed
1 0.066 0.211 0.154 0.102 specimens demonstrated a linear regime within 0.1% of strain
(in global stress-strain behavior (Figure S3), the analysis was
conducted at the same strain level.
Figure 6 presents the strain fields of the three auxetic
designs calculated via FEA (convergence analysis is
2 0.070 0.169 0.120 0.169
presented in Figure S4, and the results for pixelized cells and
the number of elements per pixel under various conditions
are presented in Tables S1 and S2), predicted with the DL
model, and calculated from the ML-aided characterization.
The selected structures were chosen arbitrarily among
3 0.132 0.215 0.294 0.141 designs possessing NPR characteristics, with NPR values
characterized by the DL model. The results demonstrate
that comparable strain field patterns are obtainable from the
three analyses. Specifically, the ML-aided characterizations
revealed pronounced strain values in the areas denoted
Figure 6. Prediction of deep learning (DL) model and experimental validation. Finite element method- and DL-predicted effective strain field, and
mechanoluminescent-transformed result at 0.1% tensile strain condition
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 56 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.3539