Page 63 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 63
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
A B C D
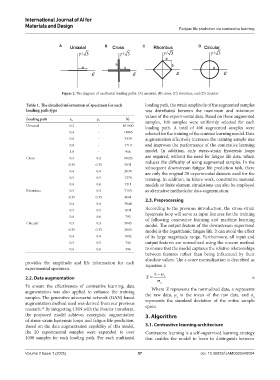
Figure 2. The diagram of multiaxial loading paths: (A) uniaxial, (B) cross, (C) rhombus, and (D) circular
Table 1. The detailed information of specimen for each loading path, the strain amplitude of the augmented samples
loading path type was distributed between the maximum and minimum
values of the experimental data. Based on these augmented
Loading path εa γa Nf samples, 100 samples were uniformly selected for each
Uniaxial 0.2 - 161000 loading path. A total of 400 augmented samples were
0.4 - 11865 selected for the training of the contrast learning model. Data
0.6 - 3339 augmentation effectively increases the training sample size
0.8 - 1719 and improves the performance of the contrastive learning
1.0 - 906 model. In addition, only stress-strain hysteresis loops
Cross 0.3 0.3 10023 are required, without the need for fatigue life data, which
0.35 0.35 5831 reduces the difficulty of using augmented samples. In the
subsequent downstream fatigue life prediction task, there
0.4 0.4 2038 are only the original 20 experimental datasets used for the
0.5 0.5 1378 training. In addition, in future work, constitutive material
0.6 0.6 1311 models or finite element simulations can also be employed
Rhombus 0.3 0.3 7193 as alternative methods for data augmentation.
0.35 0.35 4041 2.3. Preprocessing
0.4 0.4 3944
0.5 0.5 1031 According to the previous introduction, the stress-strain
0.6 0.6 795 hysteresis loop will serve as input features for the training
of following contrastive learning and machine learning
Circular 0.3 0.3 5045 model. The output feature of the downstream supervised
0.35 0.35 2963 model is the logarithmic fatigue life. It can avoid the effect
0.4 0.4 1802 of its large magnitude range. Furthermore, all input and
0.5 0.5 744 output features are normalized using the z-score method
0.6 0.6 396 to ensure that the model captures the relative relationships
between features rather than being influenced by their
absolute values. The z-score normalization is described as
provides the amplitude and life information for each Equation I:
experimental specimen.
x x
2.2. Data augmentation x (I)
x
To ensure the effectiveness of contrastive learning, data
augmentation was also applied to enhance the training Where x represents the normalized data, x represents
samples. The generative adversarial network (GAN)-based the raw data, μ is the mean of the raw data, and σ
x
x
represents the standard deviation of the entire sample
augmentation method used was derived from our previous space.
research. By integrating CNN with the Fourier transform,
16
the proposed model achieves synergistic augmentation 3. Algorithm
of stress-strain hysteresis loops and fatigue life prediction.
Based on the data augmentation capability of this model, 3.1. Contrastive learning architecture
the 20 experimental samples were expanded to over Contrastive learning is a self-supervised learning strategy
1000 samples for each loading path. For each multiaxial that enables the model to learn to distinguish between
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 57 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004