Page 64 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 64
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
similar and dissimilar samples to extract features, without In this work, contrastive learning was applied to
relying on manually labeled data In the contrastive the multiaxial fatigue life prediction of materials, using
58
.
learning framework, a pair of samples (positive and stress-strain hysteresis data as the input. Considering
negative pairs) is typically constructed, where positive that contrastive learning can reduce the distance between
pairs consist of similar or related samples and negative similar samples in the feature space, this framework
pairs consist of dissimilar samples. The model’s objective aims to extract general, discriminative features that are
is to minimize the distance between positive pairs and shared by samples with the same amplitude but different
maximize the distance between negative pairs. This learning loading paths. These features were then used to construct
approach effectively utilizes unlabeled data and enhances a downstream fatigue life prediction model. The core idea
the model’s generalization ability on real-world data. of contrastive learning was implemented by constructing
Contrastive learning has been widely applied to various positive and negative sample pairs. The construction of
tasks, such as image recognition, 59,60 natural language these pairs was done by the data augmentation module,
processing, 61,62 and audio analysis, 63,64 demonstrating which randomly selected a small batch of data containing
outstanding performance. Especially in the field of image N samples. Negative samples were not specifically sampled,
processing, contrastive learning learns powerful visual and after data augmentation, 2N data samples were
feature representations by leveraging samples generated generated. In this case, for each positive sample pair, there
from different perspectives, sizes, or other transformations were 2(N−1) corresponding negative pairs. In this study,
of images. data augmentation involved adding Gaussian noise and
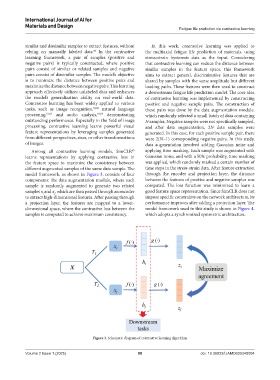
Among all contrastive learning models, SimCLR applying time masking. Each sample was augmented with
65
learns representations by applying contrastive loss in Gaussian noise, and with a 50% probability, time masking
the feature space to maximize the consistency between was applied, which randomly masked a certain number of
different augmented samples of the same data sample. The time steps in the stress-strain data. After feature extraction
model framework, as shown in Figure 3, consists of four through the encoder and projection layer, the distance
components: the data augmentation module, where each between the features of positive and negative samples was
sample is randomly augmented to generate two related computed. The loss function was minimized to learn a
samples x and x, which are then passed through an encoder good feature space representation. Since SimCLR does not
i
j
to extract high-dimensional features. After passing through impose specific constraints on the network architecture, its
a projection layer, the features are mapped to a lower- performance improves after adding a projection layer. The
dimensional space, where the contrastive loss between the model framework used in this study is shown in Figure 4,
samples is computed to achieve maximum consistency. which adopts a synchronized symmetric architecture.
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of contrastive learning algorithm
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 58 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004