Page 69 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 69
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
Based on these results, CNN1D was selected as the
encoder for the contrastive learning framework, and
the linear regression layer was used as the downstream
regression model for fatigue life prediction. This
combination not only achieved the lowest RMSE value but
also provided acceptable prediction results on the test set,
fully validating the superiority of this combination.
To further validate the effectiveness of data
augmentation in contrastive learning on the training
results, the CNN1D-based contrastive learning encoder
was chosen, and the performance of the downstream
model was compared under two conditions: with and
without data augmentation. The training loss is shown in
Figure 10. The RMSE performances of life prediction models. Figure 12. It can be observed that with data augmentation,
Abbreviations: 1D-CNN: One-dimensional convolutional neural the model achieved a sufficiently small loss after fewer
network; 2D-CNN: Two-dimensional convolutional neural network; epochs and began to converge quickly. In contrast, the
ANN: Artificial neural network; GRU: Gated recurrent unit; Linear:
Linear regression; RMSE: Root mean squared error; SVM: Support vector model without data augmentation had a relatively large
machine; XGBoost: eXtreme Gradient boosting. initial loss and required more epochs to converge.
A B
C D
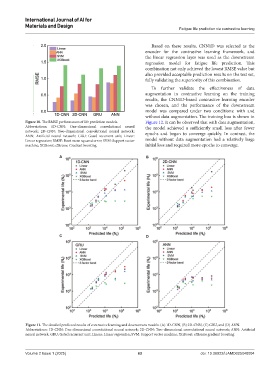
Figure 11. The detailed predicted results of contrastive learning and downstream models: (A) 1D-CNN, (B) 2D-CNN, (C) GRU, and (D) ANN.
Abbreviations: 1D-CNN: One-dimensional convolutional neural network; 2D-CNN: Two-dimensional convolutional neural network; ANN: Artificial
neural network; GRU: Gated recurrent unit; Linear: Linear regression; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost: eXtreme gradient boosting.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 63 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004