Page 73 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 73
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
A B
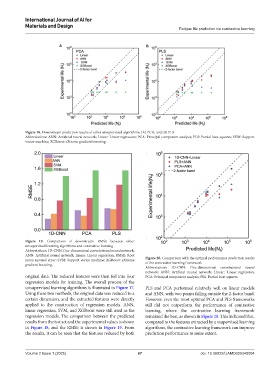
Figure 18. Downstream prediction results of other unsupervised algorithms: (A) PCA, and (B) PLS
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; Linear: Linear regression; PCA: Principal component analysis; PLS: Partial least squares; SVM: Support
vector machine; XGBoost: eXtreme gradient boosting.
Figure 19. Comparison of downstream RMSE between other
unsupervised learning algorithms and contrastive learning
Abbreviations: 1D-CNN: One-dimensional convolutional neural network;
ANN: Artificial neural network; Linear: Linear regression; RMSE: Root
mean squared error; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost: eXtreme Figure 20. Comparison with the optimal performance prediction results
gradient boosting. of the contrastive learning framework
Abbreviations: 1D-CNN: One-dimensional convolutional neural
network; ANN: Artificial neural network; Linear: Linear regression;
original data. The reduced features were then fed into four PCA: Principal component analysis; PLS: Partial least squares.
regression models for training. The overall process of the
unsupervised learning algorithms is illustrated in Figure 17. PLS and PCA performed relatively well on linear models
Using these two methods, the original data was reduced to a and ANN, with two points falling outside the 2-factor band.
certain dimension, and the extracted features were directly However, even the most optimal PCA and PLS frameworks
applied to the construction of regression models. ANN, still did not outperform the performance of contrastive
linear regression, SVM, and XGBoost were still used as the learning, where the contrastive learning framework
regression models. The comparison between the predicted remained the best, as shown in Figure 20. This indicated that,
results from the test set and the experimental values is shown compared to the features extracted by unsupervised learning
in Figure 18, and the RMSE is shown in Figure 19. From algorithms, the contrastive learning framework can improve
the results, it can be seen that the features reduced by both prediction performance to some extent.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 67 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004