Page 70 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 70
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
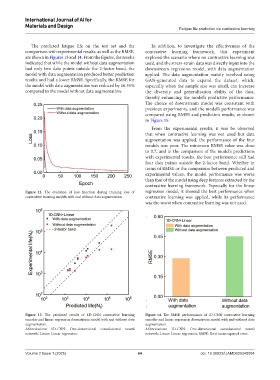
The predicted fatigue life on the test set and the In addition, to investigate the effectiveness of the
comparison with experimental results, as well as the RMSE, contrastive learning framework, this experiment
are shown in Figures 13 and 14. From the figures, the results explored the scenario where no contrastive learning was
indicated that while the model without data augmentation used, and the stress-strain data was directly input into the
had only two data points outside the 2-factor band, the downstream regression model, with data augmentation
model with data augmentation produced better prediction applied. The data augmentation mainly involved using
results and had a lower RMSE. Specifically, the RMSE for GAN-generated data to expand the dataset, which,
the model with data augmentation was reduced by 16.35% especially when the sample size was small, can increase
compared to the model without data augmentation. the diversity and generalization ability of the data,
thereby enhancing the model’s predictive performance.
The choice of downstream model was consistent with
previous experiments, and the model’s performance was
compared using RMSE and prediction results, as shown
in Figure 15.
From the experimental results, it was be observed
that when contrastive learning was not used but data
augmentation was applied, the performance of the four
models was poor. The minimum RMSE value was close
to 0.7, and in the comparison of the model’s predictions
with experimental results, the best performance still had
four data points outside the 2-factor band. Whether in
terms of RMSE or the comparison between predicted and
experimental values, the model performance was worse
than that of the model using deep features extracted by the
contrastive learning framework. Especially for the linear
Figure 12. The evolution of loss function during training loss of regression model, it showed the best performance when
contrastive learning models with and without data augmentation contrastive learning was applied, while its performance
was the worst when contrastive learning was not used.
Figure 13. The predicted results of 1D-CNN contrastive learning Figure 14. The RMSE performances of 1D-CNN contrastive learning
encoder and linear regression downstream model with and without data encoder and linear regression downstream model with and without data
augmentation. augmentation.
Abbreviations: 1D-CNN: One-dimensional convolutional neural Abbreviations: 1D-CNN: One-dimensional convolutional neural
network; Linear: Linear regression. network; Linear: Linear regression; RMSE: Root mean squared error.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 64 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004