Page 71 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 71
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
A B
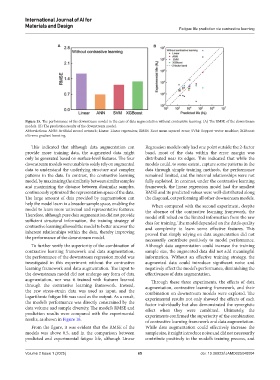
Figure 15. The performance of the downstream model in the case of data augmentation without contrastive learning. (A) The RMSE of the downstream
models. (B) The prediction results of the downstream model.
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; Linear: Linear regression; RMSE: Root mean squared error; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost:
eXtreme gradient boosting.
This indicated that although data augmentation can Regression models only had one point outside the 2-factor
provide more training data, the augmented data might band, most of the data within the error margin was
only be generated based on surface-level features. The four distributed near its edges. This indicated that while the
downstream models were unable to solely rely on augmented models could, to some extent, capture some patterns in the
data to understand the underlying structure and complex data through simple training methods, the performance
patterns in the data. In contrast, the contrastive learning remained limited, and the internal relationships were not
model, by maximizing the similarity between similar samples fully exploited. In contrast, under the contrastive learning
and maximizing the distance between dissimilar samples, framework, the linear regression model had the smallest
continuously optimized the representation space of the data. RMSE and its predicted values were well-distributed along
The large amount of data provided by augmentation can the diagonal, outperforming all other downstream models.
help the model learn in a broader sample space, enabling the When compared with the second experiment, despite
model to learn more universal and representative features. the absence of the contrastive learning framework, the
Therefore, although pure data augmentation did not provide model still relied on the limited information from the raw
sufficient structural information, the training strategy of data for training. The model depended on the data’s quality
contrastive learning allowed the model to better uncover the and complexity to learn some effective features. This
inherent relationships within the data, thereby improving proved that simply relying on data augmentation did not
the performance of the downstream model. necessarily contribute positively to model performance.
To further verify the superiority of the combination of Although data augmentation could increase the training
contrastive learning framework and data augmentation, sample size, the augmented data did not add meaningful
the performance of the downstream regression model was information. Without an effective training strategy, the
investigated in this experiment without the contrastive augmented data could introduce significant noise and
learning framework and data augmentation. The input to negatively affect the model’s performance, diminishing the
the downstream model did not undergo any form of data effectiveness of data augmentation.
augmentation, nor was it trained with features learned Through these three experiments, the effects of data
through the contrastive learning framework. Instead, augmentation, contrastive learning framework, and their
the raw stress-strain data was used as input, and the combination on downstream models were explored. The
logarithmic fatigue life was used as the output. As a result, experimental results not only showed the effects of each
the model’s performance was directly constrained by the factor individually but also demonstrated the synergistic
data volume and sample diversity. The model’s RMSE and effect when they were combined. Ultimately, the
prediction results were compared with the experimental experiments confirmed the superiority of the combination
results, as shown in Figure 16. of contrastive learning framework and data augmentation.
From the figure, it was evident that the RMSE of the While data augmentation could effectively increase the
models was above 0.5, and in the comparison between sample size, it might introduce noise and did not necessarily
predicted and experimental fatigue life, although Linear contribute positively to the model’s training process, and
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 65 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004