Page 72 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 72
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
A B
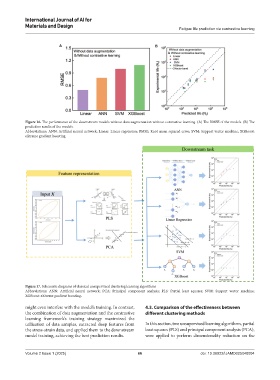
Figure 16. The performance of the downstream models without data augmentation without contrastive learning. (A) The RMSE of the models. (B) The
prediction results of the models.
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; Linear: Linear regression; RMSE: Root mean squared error; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost:
eXtreme gradient boosting.
Figure 17. Schematic diagrams of classical unsupervised clustering learning algorithms
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; PCA: Principal component analysis; PLS: Partial least squares; SVM: Support vector machine;
XGBoost: eXtreme gradient boosting.
might even interfere with the model’s training. In contrast, 4.3. Comparison of the effectiveness between
the combination of data augmentation and the contrastive different clustering methods
learning framework’s training strategy maximized the
utilization of data samples, extracted deep features from In this section, two unsupervised learning algorithms, partial
the stress-strain data, and applied them to the downstream least squares (PLS) and principal component analysis (PCA),
model training, achieving the best prediction results. were applied to perform dimensionality reduction on the
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 66 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004