Page 66 - IJAMD-2-1
P. 66
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Fatigue life prediction via contrastive learning
their ability to represent features effectively. Finally, based cycle. Therefore, to further determine which encoder
on the learned feature representations, a performance structure was more suitable for the original data, four
comparison is conducted for downstream life prediction structures—One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural
tasks, examining the predictive effectiveness across various Network (1D-CNN), Two-Dimensional Convolutional
machine learning models. Neural Network (2D-CNN), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU),
and ANN—were used. The high-dimensional features
4.1. Performance with different encoder network extracted by the encoder were passed through two fully
architectures connected layers and uniformly reduced to 64 dimensions,
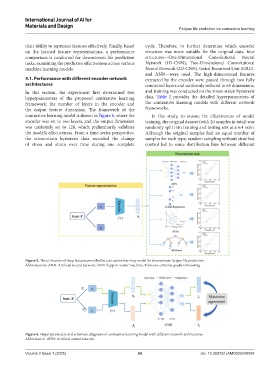
In this section, the experiment first determined two and training was conducted on the stress-strain hysteresis
hyperparameters of the proposed contrastive learning data. Table 2 provides the detailed hyperparameters of
framework: the number of layers in the encoder and the contrastive learning models with different network
the output feature dimension. The framework of the frameworks.
contrastive learning model is shown in Figure 6, where the In this study, to ensure the effectiveness of model
encoder was set to two layers, and the output dimension training, the original dataset (with 20 samples in total) was
was uniformly set to 128, which preliminarily validates randomly split into training and testing sets at a 6:4 ratio.
the model’s effectiveness. From a time-series perspective, Although the original samples had an equal number of
the stress-strain hysteresis data recorded the change samples for each type, random sampling without stratified
of stress and strain over time during one complete control led to some distribution bias between different
Figure 5. The utilization of deep features provided by contrastive learning model for downstream fatigue life prediction
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost: eXtreme gradient boosting.
Figure 6. Hyperparameters and schematic diagrams of contrastive learning model with different network architectures
Abbreviation: ANN: Artificial neural network.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 60 doi: 10.36922/IJAMD025040004