Page 342 - IJB-10-1
P. 342
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed bone scaffolds and biofilm formation
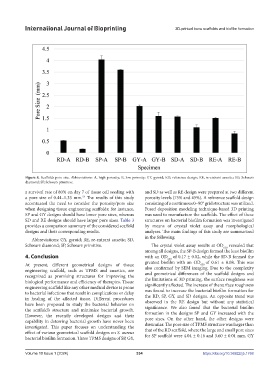
Figure 8. Scaffolds pore size. Abbreviations: A, high porosity; B, low porosity; GY, gyroid; RD, reference design; RE, re-entrant auxetic; SD, Schwarz
diamond; SP, Schwarz primitive.
a survival rate of 80% on day 7 of tissue cell seeding with and SD as well as RE design were prepared at two different
a pore size of 0.44–1.33 mm. The results of this study porosity levels (75% and 45%). A reference scaffold design
54
accentuated the need to consider the porosity/pore size consisting of a continuous 0–90° grid structure was utilized.
when designing tissue engineering scaffolds; for instance, Fused deposition modeling technique-based 3D printing
SP and GY designs should have lower pore sizes, whereas was used to manufacture the scaffolds. The effect of these
SD and RE designs should have larger pore sizes. Table 3 structures on bacterial biofilm formation was investigated
provides a comparison summary of the considered scaffold by means of crystal violet assay and morphological
designs and their corresponding results. analyses. The main findings of this study are summarized
in the following:
Abbreviations: GY, gyroid; RE, re-entrant auxetic; SD,
Schwarz diamond; SP, Schwarz primitive. The crystal violet assay results at OD revealed that
630
among all designs, the SP-B design formed the least biofilm
4. Conclusion with an OD of 0.17 ± 0.02, while the SD-B formed the
630
At present, different geometrical designs of tissue greatest biofilm with an OD 630 of 0.61 ± 0.08. This was
engineering scaffold, such as TPMS and auxetics, are also confirmed by SEM imaging. Due to the complexity
recognized as promising structures for improving the and geometrical differences of the scaffold designs and
biological performance and efficiency of therapies. Tissue the limitations of 3D printing, the surface roughness was
engineering scaffold like any other medical device is prone significantly affected. The increase of the surface roughness
to bacterial infections that result in complications or delay was found to increase the bacterial biofilm formation for
in healing of the affected tissue. Different procedures the RD, SP, GY, and SD designs. An opposite trend was
have been proposed to study the bacterial behavior on observed in the RE design but without any statistical
the scaffold’s structure and minimize bacterial growth. significance. We also found that the bacterial biofilm
However, the recently developed designs and their formation in the designs SP and GY increased with the
capability in deterring bacterial growth have never been pore sizes. On the other hand, the other designs were
investigated. This paper focuses on understanding the dissimilar. The pore size of TPMS structure was larger than
effect of various geometrical scaffold designs on S. aureus that of the RD scaffold, where the large and small pore sizes
bacterial biofilm formation. Three TPMS designs of SP, GY, for SP scaffold were 4.04 ± 0.16 and 3.60 ± 0.01 mm, GY
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 334 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1768