Page 421 - IJB-10-1
P. 421
International Journal of Bioprinting Osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs by PBF-LB
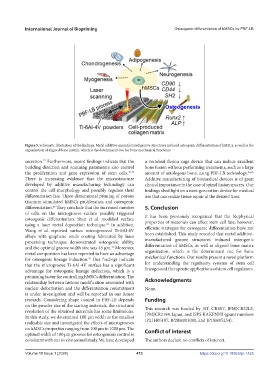
Figure 5. Schematic illustration of the findings. Metal additive-manufactured groove structures induced osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs, as well as the
organization of aligned bone matrix, which is the determinant cue for bone mechanical functions.
secretion. Furthermore, recent findings indicate that the a vertebral fusion cage device that can induce excellent
37
building direction and scanning parameters also control bone fusion without performing treatments, such as a large
the proliferation and gene expression of stem cells. 38,39 amount of autologous bone, using PBF-LB technology. 24,25
There is increasing evidence that the microstructure Additive manufacturing of biomedical devices is of great
developed by additive manufacturing technology can clinical importance in the case of spinal fusion spacers. Our
control the cell morphology and possibly regulate their findings shed light on a next-generation device for medical
differentiation fate. Three-dimensional printing of porous use that can realize tissue repair at the desired time.
titanium stimulated hMSCs proliferation and osteogenic
differentiation. They conclude that the increased number 5. Conclusion
40
of cells on the microgroove surface possibly triggered
osteogenic differentiation. Shen et al. modified surface It has been previously recognized that the biophysical
properties of materials can affect stem cell fate; however,
using a laser metal deposition technique. In addition,
41
Wang et al. reported surface microgrooved Ti-6Al-4V efficient strategies for osteogenic differentiation have not
alloys with graphene oxide coating fabricated by laser been established. This study revealed that metal additive-
processing technique demonstrated osteogenic ability, manufactured groove structures induced osteogenic
and the optimal groove width size was 45 μm. Moreover, differentiation of hMSCs, as well as aligned bone matrix
42
metal composition has been reported to have an advantage organization, which is the determinant cue for bone
for osteogenic lineage induction. Our findings indicate mechanical functions. Our results present a novel platform
43
that the microgroove Ti-6Al-4V surface has a significant for understanding the regulatory systems of stem cell
advantage for osteogenic lineage induction, which is a lineages and therapeutic applications of stem cell regulators.
promising factor for controlling hMSCs differentiation. The
relationship between histone modification associated with Acknowledgments
nuclear deformation and the differentiation commitment None.
is under investigation and will be reported in our future
research. Considering shape control in PBF-LB depends Funding
on the powder size of the starting materials, the structural
resolution of the obtained materials has some limitations. This research was funded by JST, CREST, JPMJCR22L5,
JPMJCR2194, Japan, and JSPS KAKENHI (grant numbers
In this study, we determined 100 μm width as the smallest
realizable size and investigated the effects of microgrooves JP21H05197, JP20H003080, and JP18H05254).
on hMSCs properties ranging from 100 μm to 1000 μm. The
optimal width of 100 μm grooves for osteogenesis control is Conflict of interest
consistent with our in vivo animal study. We have developed The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 413 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.1425