Page 249 - IJB-10-2
P. 249
International Journal of Bioprinting G40T60@WNT5A promotes osteoblast differentiation
the PBS group, the G40T60 and WNT5A groups displayed
significant ALP and ARS staining intensity, indicating
that G40T60 and WNT5A significantly promoted
BMSCs osteogenic differentiation. Furthermore, BMSCs
osteogenic differentiation was significantly enhanced
in the G40T60@WNT5A group, as compared with the
G40T60 and WNT5A groups (Figure 8A and B).
Furthermore, using RT-qPCR and Western blot, we
were able to detect the expression levels of osteogenic
differentiation markers, such as Runx2, Osterix, Alpl, Opn,
and Ocn, in BMSCs. The results showed that the expression
levels of osteogenic differentiation markers in the G40T60
and WNT5A groups were significantly increased compared
to the PBS group. Moreover, compared with the G40T60
and WNT5A groups, the expression levels of osteogenic
differentiation markers in the G40T60@WNT5A group were
significantly elevated (Figure 8C and D). H&E staining was
used to examine the formation of induced membranes. The
results showed that the G40T60@WNT5A group contained
many cells and formed abundant parallel fibrous tissue
with the scaffold (as indicated by the arrows in the image).
The microvascular network was also highly developed. The
number of cells and microvessel count in the G40T60 and
WNT5A groups were lower than in the G40T60@WNT5A
group. No significant microvessel formation was observed
in the PBS control group (Figure 8E).
The above results indicated that after G40T60 was
loaded with WNT5A, it could significantly promote the
osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs.
3.9. Induced membrane formed by G40T60@WNT5A
scaffold could promote angiogenesis in CTO&BD rats
Next, we continued to investigate whether the induced
membrane formed by G40T60@WNT5A could promote
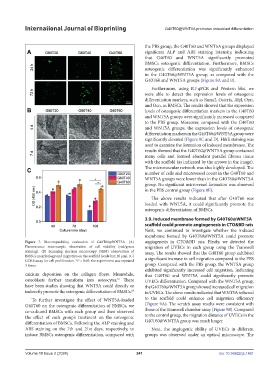
Figure 7. Biocompatibility evaluation of G40T60@WNT5A. (A) angiogenesis in CTO&BD rats. Firstly, we detected the
Fluorescence microscopic observation of cell viability (red/green migration of UVECs in each group using the Transwell
staining). (B) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation of assay. The results showed that the G40T60 group exhibited
BMSCs morphology and migration on the scaffold (scale bar: 20 μm). (C) a significant increase in cell migration compared to the PBS
CCK8 assay for cell proliferation. *P < 0.05; the experiment was repeated
3 times. group. Compared with the PBS group, the WNT5A group
exhibited significantly increased cell migration, indicating
calcium deposition on the collagen fibers. Meanwhile, that G40T60 and WNT5A could significantly promote
osteoblasts further transform into osteocytes. There UVECs differentiation. Compared with the WNT5A group,
67
have been studies showing that WNT5A could directly or the G40T60@WNT5A group showed increased cell migration
indirectly promote the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. 68 in UVECs. The above results indicated that WNT5A tethered
To further investigate the effect of WNT5A-loaded to the scaffold could enhance cell migration efficiency
G40T60 on the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, we (Figure 9A). The scratch assay results were consistent with
co-cultured BMSCs with each group and then observed those of the Transwell chamber assay (Figure 9B). Compared
the effect of each group’s treatment on the osteogenic to the control group, the migration distance of UVECs in the
differentiation of BMSCs. Following the ALP staining and G40T60@WNT5A group was much longer.
ARS staining on the 7th and 21st days, respectively, to Next, the angiogenic ability of UVECs in different
induce BMSCs osteogenic differentiation, compared with groups was observed under an optical microscope. The
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 241 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1461