Page 57 - IJB-10-2
P. 57
International Journal of Bioprinting Advancements in 3D printing
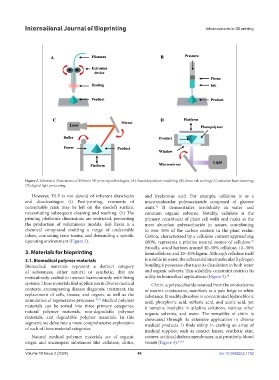
Figure 2. Schematic illustrations of different 3D printing technologies. (A) Fused deposition modeling; (B) direct ink writing; (C) selective laser sintering;
(D) digital light processing.
However, DLP is not devoid of inherent drawbacks and hyaluronic acid. For example, cellulose is as a
and disadvantages: (i) Post-printing, remnants of macromolecular polysaccharide composed of glucose
consumable resin may be left on the model’s surface, units. It demonstrates insolubility in water and
32
necessitating subsequent cleaning and washing. (ii) The common organic solvents. Notably, cellulose is the
printing platform’s dimensions are restricted, preventing primary constituent of plant cell walls and ranks as the
the production of voluminous models. (iii) Resin is a most abundant polysaccharide in nature, contributing
chemical compound emitting a range of undesirable to over 50% of the carbon content in the plant realm.
odors, containing trace toxins, and demanding a specific Cotton, characterized by a cellulose content approaching
operating environment (Figure 2). 100%, represents a pristine natural source of cellulose.
33
Broadly, wood harbors around 40–50% cellulose, 10–30%
3. Materials for bioprinting hemicellulose, and 20–30% lignin. Although cellulose itself
3.1. Biomedical polymer materials is soluble in water, the substantial intermolecular hydrogen
Biomedical materials represent a distinct category bonding it possesses obstructs its dissolution in both water
of substances, either natural or synthetic, that are and organic solvents. This solubility constraint restricts its
meticulously crafted to interact harmoniously with living utility in biomedical applications (Figure 3). 34
systems. These materials find application in diverse medical Chitin, a polysaccharide sourced from the exoskeletons
contexts, encompassing disease diagnosis, treatment, the of marine crustaceans, manifests as a pale beige to white
replacement of cells, tissues, and organs, as well as the substance. It readily dissolves in concentrated hydrochloric
stimulation of regenerative processes. 30,31 Medical polymer acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, and acetic acid, yet
materials can be sorted into three primary categories: it remains insoluble in alkaline solutions, various other
natural polymer materials, non-degradable polymer organic solvents, and water. The versatility of chitin is
materials, and degradable polymer materials. In this showcased through its extensive application in diverse
segment, we delve into a more comprehensive exploration medical products. It finds utility in crafting an array of
of each of these material categories.
medical supplies, such as contact lenses, synthetic skin,
Natural medical polymer materials are of organic sutures, artificial dialysis membranes, and prosthetic blood
origin and encompass substances like cellulose, chitin, vessels (Figure 4). 35,36
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 49 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1752