Page 155 - IJB-10-3
P. 155
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bone: Current & future
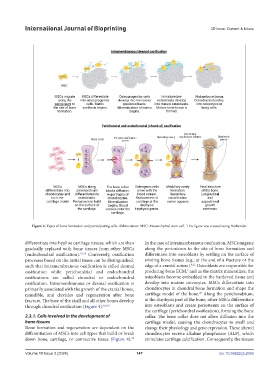
Figure 4. Types of bone formation and participating cells. Abbreviation: MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell. This figure was created using BioRender.
differentiate into hyaline cartilage tissues, which are then In the case of intramembranous ossification, MSCs migrate
gradually replaced with bone tissues from other MSCs along the periosteum to the site of bone formation and
(endochondral ossification). 19,20 Conversely, ossification differentiate into osteoblasts by settling on the surface of
processes based on the initial tissue can be distinguished, existing bone tissues (e.g., at the end of a fracture or the
8,21
such that intramembranous ossification is called desmal edge of a cranial suture). Osteoblasts are responsible for
ossification while perichondrial and endochondral producing bone ECM, and as the matrix mineralizes, the
9
ossifications are called chondral or endochondral osteoblasts become embedded in the hardened tissue and
ossification. Intramembranous or desmal ossification is develop into mature osteocytes. MSCs differentiate into
primarily associated with the growth of the cranial bones, chondrocytes in chondral bone formation and shape the
20
mandible, and clavicles and regeneration after bone cartilage model of the bone. Along the perichondrium,
fracture. The base of the skull and all other bones develop at the diaphysis part of the bone, other MSCs differentiate
through chondral ossification (Figure 4). 8,9,19 into osteoblasts and create periosteum on the surface of
the cartilage (perichondral ossification), forming the bone
2.3.1. Cells involved in the development of collar. The bone collar does not allow diffusion into the
bone tissues cartilage model, causing the chondrocytes to swell and
Bone formation and regeneration are dependent on the change their physiology and gene expression. These altered
differentiation of MSCs into cell types that build or break chondrocytes secrete alkaline phosphatase (ALP), which
down bone, cartilage, or connective tissue (Figure 4). stimulates cartilage calcification. Consequently, the tissues
20
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 147 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2056