Page 616 - IJB-10-3
P. 616
International Journal of Bioprinting Wireless module system applied on 3D-printed implant
Table 1. Material properties input to FE analysis for aluminum bone). Those contours were extracted and converted to
alloy cantilever beam reconstruct a 3D solid model of the mandible bone with
Material Young’s modulus (GPa) Poisson’s ratio segmental defect.
Aluminum plate 70 0.33 The segmental reconstructed implant was designed
Aluminum extrusion 70 0.33 according to the previous work, i.e., (1) the implant body
Screw 200 0.3 is equipped with shell structure of 0.5 mm thickness to
reduce the implant weight, (2) the height of the implant
device. The strain values ratio between points A and B was is half of the height of the bone segment, and (3) the bone
calculated, and the percentage error between this ratio and graft space for postoperative prosthesis is reserved at the
the theoretical value (theoretical strain at point A being top for subsequent follow-up. The implant thickness was
twice that of point B) was determined (Table 1). two-third of the bone segment thickness to make space for
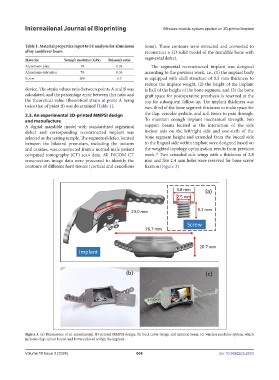
2.3. An experimental 3D-printed MMPSI design the flap, vascular pedicle, and soft tissue to pass through.
and manufacture To maintain enough implant mechanical strength, two
A digital mandible model with standardized segmental support beams located at the interaction of the side
defect and corresponding reconstructed implant was incisor axis on the left/right side and one-sixth of the
selected as the testing sample. The segmental defect located bone segment height and extended from the buccal side
between the bilateral premolars, including the incisors to the lingual side within implant were designed based on
and canines, was constructed from a normal male patient the weighted topology optimization results from previous
computed tomography (CT) scan data. All DICOM CT work. Two extended side wings with a thickness of 2.8
12
cross-section image data were processed to identify the mm and five 2.4 mm holes were reserved for bone screw
contours of different hard tissues (cortical and cancellous fixation (Figure 3).
Figure 3. (a) Dimensions of an experimental 3D-printed MMPSI design; (b) back cover design and internal beam; (c) wireless modulus system, which
includes chip, circuit board, and battery placed within the implant.
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 608 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2553