Page 101 - IJB-4-1
P. 101
Pre-clinical evaluation of advanced nerve guide conduits using a novel 3D in vitro testing model
neuronal cells was observed between PCL films and
TCP. Taken together, microfibres supported the
alignment of neuronal cells, yielded in living cell
numbers greater than 90% and yielded in higher
numbers of living cells compared to the flat PCL
control.
3.4 Ex vivo dorsal root ganglion culture
Schwann cell proliferation and migration from the
proximal to the distal nerve stump is one major key
event in peripheral nerve regeneration to provide
guidance for re-growing axons in order to successfully
reinnervate target effectors on distal site.
Simulating the proximal injury site in vitro, a rat
dorsal root ganglion was placed on top of the
example NGC device for investigations on internal
scaffold performance by analysing Schwann cell
proliferation and axon outgrowth along the
microfibre scaffold from the explant towards the
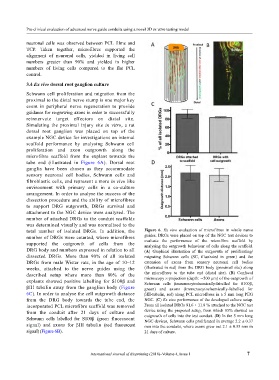
tube end (illustrated in Figure 6A). Dorsal root
ganglia have been chosen as they accommodate
sensory neuronal cell bodies, Schwann cells and
fibroblastic cells, and represent a more in vivo like
environment with primary cells in a co-culture
arrangement. In order to analyse the success of the
dissection procedure and the ability of microfibres
to support DRG outgrowth, DRGs survival and
attachment to the NGC device were analysed. The
number of attached DRGs to the conduit scaffolds
was determined visually and was normalised to the
total number of isolated DRGs. In addition, the Figure 6. Ex vivo evaluation of microfibres in whole nerve
number of DRGs were counted, where microfibres guides. DRGs were placed on top of the NGC test devices to
evaluate the performance of the microfibre scaffold by
supported the outgrowth of cells from the analysing the outgrowth behaviour of cells along the scaffold.
DRG body and numbers expressed in relation to all (A) Graphical illustration of the outgrowth of proliferating/
dissected DRGs. More than 90% of all isolated migrating Schwann cells (SC, illustrated in green) and the
DRGs from male Wistar rats, in the age of 10–12 extension of axons from sensory neuronal cell bodies
weeks, attached to the nerve guides using the (illustrated in red) from the DRG body (proximal site) along
described setup where more than 80% of the the microfibres to the tube end (distal site). (B) Confocal
microscopy z-projection (depth: ∼500 µm) of the outgrowth of
explants showed positive labelling for S100β and Schwann cells (immunocytochemically-labelled for S100β,
βIII tubulin away from the ganglion body (Figure green) and axons (immunocytochemically-labelled for
6C). In order to analyse the cell outgrowth distance βIII-tubulin, red) along PCL microfibres in a 5 mm long PEG
from the DRG body towards the tube end, the NGC. (C) Ex vivo performance of the developed culture setup.
incorporated PCL microfibre scaffold was removed From all isolated DRGs 91.6 ± 11.8 % attached to the NGC test
from the conduit after 21 days of culture and device using the proposed setup, from which 85% showed an
outgrowth of cells into the test conduit. (D) In the 5 mm long
Schwann cells labelled for S100β (green fluorescent NGC devices, Schwann cells proliferated in average 2.2 ± 0.37
signal) and axons for βIII tubulin (red fluorescent mm into the conduits, where axons grew out 2.1 ± 0.33 mm in
signal) (Figure 6B). 21 days of culture.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 1 7