Page 200 - IJB-10-4
P. 200
International Journal of Bioprinting Horsetail-inspired lattice for bone use
Six load cases, in strain, namely, ε , ε , ε , γ , γ , and
22
11
22
12
33
γ , in unity magnitude were applied to the RVE. The result D 2 + D D −2 D 2
13
is then homogenized to evaluate the stiffness tensor, D , E lattice = 1111 1111 1122 1122 (VII)
ijkl
given by Equation V. D 1111 + D 1122
D 2 D
(V) A = 1212 = 1212 (VIII)
D in plane− D 1111 − D 1122
Equation V may be simplified into Equation VI given It should be noted that the relative elastic E relative
that the lattice design in our study is orthotropic in nature modulus is obtained by normalizing E lattice with the
since it is invariant 90° to the principal axes. reference elastic modulus. The Zener Anisotropy Index,
A, is given by Equation VIII. The Zener Anisotropy
Index yields unity when the RVE is isotropic, while a
deviation in either the positive or negative range signifies
anisotropy. Additionally, the total exposed surface area as
30
well as the φ may be determined through computer-aided
(VI) design application.
2.3. Sample fabrication and lattice matrices
performance validation
We also performed compression testing to validate the
performance of the simulated results. The principal
Following the determination of the stress tensor, parameters of the samples selected for the test were based
with the incorporation of Lamé constants, E lattice may on sample 115r025t since the result from the simulation
be evaluated. exhibited characteristics of A close to unity and vf of
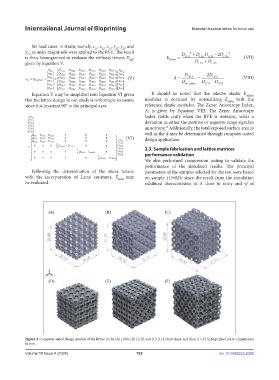
Figure 4. Computer-aided design models of the lattice in the (A) [100], (B) [110], and (C) [111] directions, and their (D–F) SLM-printed parts. Dimensions
in mm.
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 192 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2326