Page 203 - IJB-10-4
P. 203
International Journal of Bioprinting Horsetail-inspired lattice for bone use
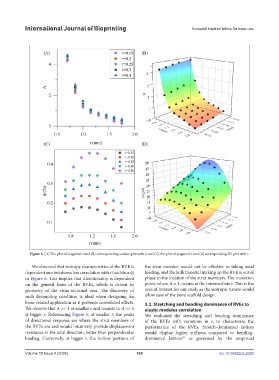
Figure 6. (A) The plot of A against r and (B) corresponding surface plot with t; and (C) the plot of φ against r and (d) corresponding 3D plot with t.
We observed that isotropy characteristics of the RVE is the strut member would not be effective in taking axial
dependent on r but shows less correlation with t (and thus φ) loading, and the bulk material making up the RVE is out of
in Figure 6. This implies that directionality is dependent phase to the location of the strut members. The transition
on the general form of the RVEs, which is driven by point, where A ≈ 1, occurs at the intermediate r. This is the
geometry of the cross-sectional area. The discovery of area of interest for our study as the isotropic nature would
such decoupling condition is ideal when designing for allow ease of the bone scaffold design.
bone-related application as it prevents convoluted effects. 3.2. Stretching and bending dominance of RVEs to
We observe that A >> 1 at smaller r and transits to A << 1 elastic modulus correlation
at bigger r. Referencing Figure 5, at smaller r, the peaks We evaluated the stretching and bending dominance
of directional response are where the strut members of of the RVEs with variations in r, to characterize the
the RVEs are and would intuitively provide displacement performance of the RVEs. Stretch-dominated lattices
resistance in the axial direction, better than perpendicular would display higher stiffness compared to bending-
loading. Conversely, at bigger r, the hollow portions of dominated lattices as governed by the empirical
38
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 195 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2326