Page 241 - IJB-10-4
P. 241
International Journal of Bioprinting N-PLN hydrogels for human skin modeling
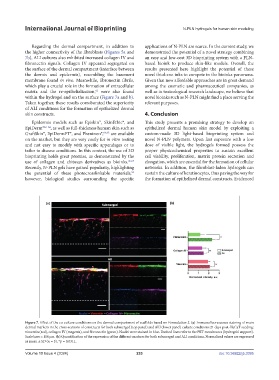
Regarding the dermal compartment, in addition to applications of N-PLN are scarce. In the current study, we
the higher connectivity of the fibroblasts (Figures 5a and demonstrated the potential of a novel strategy combining
7b), ALI cultures also exhibited increased collagen IV and an easy and low-cost 3D bioprinting system with a PLN-
fibronectin signals. Collagen IV appeared segregated on based bioink to produce skin-like models. Overall, the
the surface of the dermal compartment (interface between results presented here highlight the potential of these
the dermis and epidermis), resembling the basement novel thiol-ene inks to compete in the bioinks panorama.
membrane found in vivo. Meanwhile, fibronectin fibrils, Given that new affordable approaches are in great demand
which play a crucial role in the formation of extracellular among the cosmetic and pharmaceutical companies, as
matrix and the re-epithelialization, were also found well as in toxicological research landscape, we believe that
61
within the hydrogel and on the surface (Figure 7a and b). novel bioinks such as N-PLN might find a place serving the
Taken together, these results corroborated the superiority relevant purposes.
of ALI conditions for the formation of epithelized dermal
skin constructs. 4. Conclusion
Epidermis models such as Episkin™, SkinEthic®, and This study presents a promising strategy to develop an
EpiDerm® 62–64 , as well as full-thickness human skin such as epithelized dermal human skin model by exploiting a
GraftSkin®, EpiDermFT®, and Pheninon®, 64,65 are available custom-made 3D light-based bioprinting system and
on the market, but they are very costly for in vitro testing novel N-PLN polymers. Upon fast exposure with a low
and not easy to modify with specific appendages or to dose of visible light, the hydrogels formed possess the
tailor to disease conditions. In this context, the use of 3D proper physicochemical properties to sustain excellent
bioprinting holds great promise, as demonstrated by the cell viability, proliferation, matrix protein secretion and
use of collagen and chitosan derivatives as bioinks. 66,67 elongation, which are essential for the formation of cellular
Recently, N-PLN gels have gained popularity, highlighting networks. In addition, the fibroblast-laden hydrogels can
the potential of these photocrosslinkable materials; sustain the culture of keratinocytes, thus paving the way for
53
however, biological studies surrounding the specific the formation of epithelized dermal constructs. Evidenced
Figure 7. Effect of the co-culture conditions on the dermal compartment of scaffolds based on Formulation 2. (a) Immunofluorescence staining of main
dermal markers in the cross-sections of constructs for both submerged (top panel) and ALI (lower panel) culture conditions 21 days post-HaCaT seeding:
vimentin (red), collagen IV (magenta), and fibronectin (green). Nuclei were stained in blue. Dashed lines refer to the PET membranes (hydrogels’ support).
Scale bars = 100 µm. (b) Quantification of the expression of the different markers for both submerged and ALI conditions. Normalized values are expressed
as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p = 0.0311.
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 233 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3395