Page 565 - IJB-10-4
P. 565
International Journal of Bioprinting Light-based muscle bioprinting with bioglass
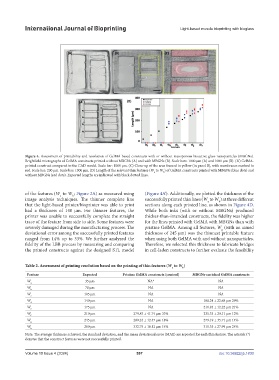
Figure 4. Assessment of printability and resolution of GelMA-based constructs with or without mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles (MBGNs).
Brightfield micrographs of GelMA constructs printed without MBGNs (A) and with MBGNs (B). Scale bars: 1000 µm (A) and 1000 µm (B). (A’) GelMA-
printed construct compared to the CAD model. Scale bar: 1000 μm. (C) Close-up of the area framed in yellow (in panel B), with membranes marked in
red. Scale bar: 200 μm. Scale bar: 1000 μm. (D) Length of the relevant thin features (W to W ) of GelMA constructs printed with MBGNs (blue dots) and
a
h
without MBGNs (red dots). Expected lengths are indicated with black dotted lines.
of the features (W to W ; Figure 2A) as measured using (Figure 4A’). Additionally, we plotted the thickness of the
a
h
image analysis techniques. The thinner complete line successfully printed thin lines (W to W ) at three different
h
a
that the light-based printer/bioprinter was able to print sections along each printed line, as shown in Figure 4D.
had a thickness of 140 µm. For thinner features, the While both inks (with or without MBGNs) produced
printer was unable to successfully complete the straight thicker-than-intended constructs, the fidelity was higher
trace of the feature from side to side. Some features were for the lines printed with GelMA with MBGNs than with
severely damaged during the manufacturing process. The pristine GelMA. Among all features, W (with an aimed
g
deviational error among the successfully printed features thickness of 245 µm) was the thinnest printable feature
ranged from 14% up to 33%. We further analyzed the when using both GelMA with and without nanoparticles.
fidelity of the LBB process by measuring and comparing Therefore, we selected this thickness to fabricate bridges
the printed constructs against the designed STL model in cell-laden constructs to further evaluate the feasibility
Table 2. Assessment of printing resolution based on the printing of thin features (W to W )
a h
Feature Expected Pristine GelMA constructs (control) MBGNs-enriched GelMA constructs
W 35 µm NA* NA
a
W b 70 µm NA NA
W c 105 µm NA NA
W 140 µm NA 180.24 ± 22.68 µm 29%
d
W 175 µm NA 211.83 ± 12.22 µm 21%
e
W 210 µm 279.83 ± 41.74 µm 33% 235.33 ± 20.11 µm 12%
f
W 245 µm 289.24 ± 12.47 µm 18% 279.19 ± 35.71 µm 14%
g
W h 280 µm 332.75 ± 18.12 µm 14% 311.35 ± 27.99 µm 24%
Note: The average thickness achieved, the standard deviation, and the mean deviational error (MAE) are reported for each thin feature. The asterisk (*)
denotes that the construct features were not successfully printed.
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 557 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1830