Page 427 - IJB-10-5
P. 427
International Journal of Bioprinting Stability of 3D-printed PEO tablets
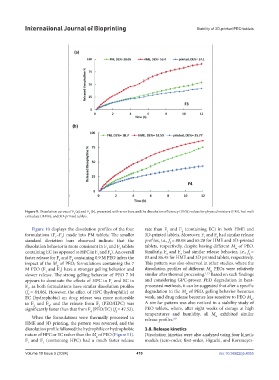
Figure 9. Dissolution curves of F (a) and F (b), presented with error bars and the dissolution efficiency (DE%) values for physical mixture (PM), hot-melt
4
3
extrudate (HME), and 3D-printed tablets.
Figure 10 displays the dissolution profiles of the four rate than F and F (containing EC) in both HME and
4
3
formulations (F –F ) made into PM tablets. The smaller 3D-printed tablets. Moreover, F and F had similar release
4
1
1
2
standard deviation bars observed indicate that the profiles, i.e., f = 88.08 and 65.28 for HME and 3D-printed
2
dissolution behavior is more consistent in F and F tablets tablets, respectively, despite having different M of PEO.
3
w
4
containing EC (as opposed to HPC in F and F ). An overall Similarly, F and F had similar release behavior, i.e., f =
1
2
2
4
3
faster release for F and F containing 0.9 M PEO infers the 83 and 86.45 for HME and 3D printed tablets, respectively.
2
4
impact of the M of PEO; formulations containing the 7 This pattern was also observed in other studies, where the
w
M PEO (F and F ) have a stronger gelling behavior and dissolution profiles of different M PEOs were relatively
w
3
1
slower release. The strong gelling behavior of PEO 7 M similar after thermal processing. Based on such findings
1,13
appears to dominate the effects of HPC in F and EC in and considering GPC-proven PEO degradation in heat-
1
F , as both formulations have similar dissolution profiles processed methods, it can be suggested that after a specific
3
(f = 84.86). However, the effect of HPC (hydrophilic) or degradation in the M of PEO, gelling behavior becomes
w
2
EC (hydrophobic) on drug release was more noticeable weak, and drug release becomes less sensitive to PEO M .
w
in F and F , and the release from F (PEO/HPC) was A similar pattern was also noticed in a stability study of
4
2
2
significantly faster than that from F (PEO/EC) (f = 47.53). PEO tablets, where, after eight weeks of storage at high
4 2 temperatures and humidity, all M exhibited similar
When the formulations were thermally processed in release profiles. 8,9 w
HME and 3D printing, the pattern was reversed, and the
dissolution profile followed the hydrophilic or hydrophobic 3.8. Release kinetics
nature of HPC or EC rather than the M of PEO (Figure 11). Dissolution kinetics were also analyzed using four kinetic
w
F and F (containing HPC) had a much faster release models (zero-order, first-order, Higuchi, and Korsmeyer-
1
2
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 419 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4055