Page 105 - IJB-6-1
P. 105
Shuai, et al.
A B C
D E F
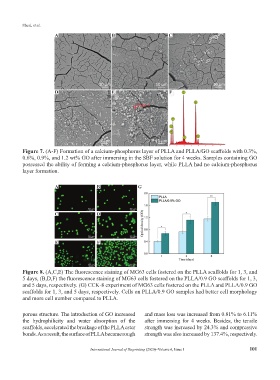
Figure 7. (A-F) Formation of a calcium-phosphorus layer of PLLA and PLLA/GO scaffolds with 0.3%,
0.6%, 0.9%, and 1.2 wt% GO after immersing in the SBF solution for 4 weeks. Samples containing GO
possessed the ability of forming a calcium-phosphorus layer, while PLLA had no calcium-phosphorus
layer formation.
A B G
C D
E F
Figure 8. (A,C,E) The fluorescence staining of MG63 cells fostered on the PLLA scaffolds for 1, 3, and
5 days, (B,D,F) the fluorescence staining of MG63 cells fostered on the PLLA/0.9 GO scaffolds for 1, 3,
and 5 days, respectively. (G) CCK-8 experiment of MG63 cells fostered on the PLLA and PLLA/0.9 GO
scaffolds for 1, 3, and 5 days, respectively. Cells on PLLA/0.9 GO samples had better cell morphology
and more cell number compared to PLLA.
porous structure. The introduction of GO increased and mass loss was increased from 0.81% to 6.11%
the hydrophilicity and water absorption of the after immersing for 4 weeks. Besides, the tensile
scaffolds, accelerated the breakage of the PLLA ester strength was increased by 24.3% and compressive
bonds. As a result, the surface of PLLA became rough strength was also increased by 137.4%, respectively.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1 101