Page 97 - IJB-6-2
P. 97
Kolan, et al.
A B
C D
Figure 8. Percentage of new bone tissue
formation in cubic and diamond scaffolds
quantified based on the total defect area. The E F
bone growth between scaffold designs with or
without bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2)
was not statistically different. The bone formation
in defects treated with BMP-2 was statistically
significant (P = 0).
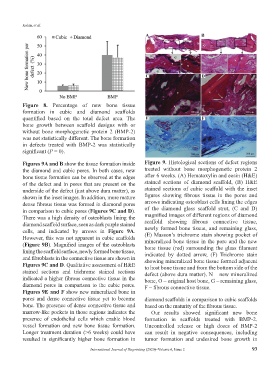
Figures 9A and B show the tissue formation inside Figure 9. Histological sections of defect regions
the diamond and cubic pores. In both cases, new treated without bone morphogenetic protein 2
bone tissue formation can be observed at the edges after 6 weeks. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)
of the defect and in pores that are present on the stained sections of diamond scaffold, (B) H&E
underside of the defect (just above dura matter), as stained sections of cubic scaffold with the inset
shown in the inset images. In addition, more mature figures showing fibrous tissue in the pores and
dense fibrous tissue was formed in diamond pores arrows indicating osteoblast cells lining the edges
in comparison to cubic pores (Figures 9C and D). of the diamond glass scaffold strut, (C and D)
There was a high density of osteoblasts lining the magnified images of different regions of diamond
diamond scaffold surface, seen as dark purple stained scaffold showing fibrous connective tissue,
cells, and indicated by arrows in Figure 9A. newly formed bone tissue, and remaining glass,
(E) Masson’s trichrome stain showing pocket of
However, this was not apparent in cubic scaffolds mineralized bone tissue in the pore and the new
(Figure 9B). Magnified images of the osteoblasts bone tissue (red) surrounding the glass filament
lining the scaffold surface, newly formed bone tissue, indicated by dotted arrow, (F) Trichrome stain
and fibroblasts in the connective tissue are shown in showing mineralized bone tissue formed adjacent
Figures 9C and D. Qualitative assessment of H&E to host bone tissue and from the bottom side of the
stained sections and trichrome stained sections defect (above dura matter). N – new mineralized
indicated a higher fibrous connective tissue in the bone, O – original host bone, G – remaining glass,
diamond pores in comparison to the cubic pores. F – fibrous connective tissue.
Figures 9E and F show new mineralized bone in
pores and dense connective tissue yet to become diamond scaffolds in comparison to cubic scaffolds
bone. The presence of dense connective tissue and based on the maturity of the fibrous tissue.
marrow-like pockets in those regions indicates the Our results showed significant new bone
presence of endothelial cells which enable blood formation in scaffolds treated with BMP-2.
vessel formation and new bone tissue formation. Uncontrolled release or high doses of BMP-2
Longer treatment duration (>6 weeks) could have can result in negative consequences, including
resulted in significantly higher bone formation in tumor formation and undesired bone growth in
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 2 93