Page 319 - IJB-10-6
P. 319
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted plasma biocarriers for MSC delivery
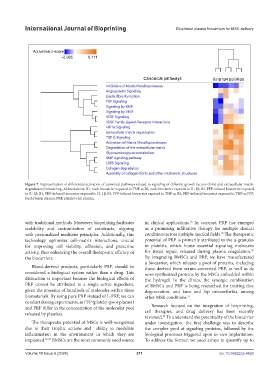
Figure 7. Representation of differential activation of canonical pathways related to signaling of different growth factors (GFs) and extracellular matrix
degradation/remodeling. Abbreviations: B1, nude biocarrier exposed to TNF-α; B2, nude biocarrier exposed to IL-1β; B3, FFP-infused biocarrier exposed
to IL-1β; B4, PRP-infused biocarrier exposed to IL-1β; B5, FFP-infused biocarrier exposed to TNF-α; B6, PRP-infused biocarrier exposed to TNF-α; FFP,
fresh frozen plasma; PRP, platelet-rich plasma.
28
with traditional methods. Moreover, bioprinting facilitates in clinical applications. In contrast, PRP has emerged
scalability and customization of constructs, aligning as a promising infiltrative therapy for multiple clinical
29
with personalized medicine principles. Additionally, this conditions across multiple medical fields. The therapeutic
technology optimizes cell–matrix interactions, crucial potential of PRP is primarily attributed to the α-granules
for improving cell viability, adhesion, and paracrine in platelets, which house essential signaling molecules
30
activity, thus enhancing the overall therapeutic efficacy of for tissue repair, released during plasma coagulation.
the biocarriers. By integrating BMSCs and PRP, we have manufactured
a biocarrier, which releases a pool of proteins, including
Blood-derived products, particularly PRP, should be those derived from serum-converted PRP, as well as de
considered a biological system rather than a drug. This novo synthesized proteins by the MSCs embedded within
distinction is important because the biological effects of the hydrogel. In the clinics, the synergic combination
PRP cannot be attributed to a single active ingredient, of BMSCs and PRP is being researched for treating disc
given the presence of hundreds of molecules within these degeneration, and knee and hip osteoarthritis, among
biomaterials. By using pure PRP instead of L-PRP, we can other MSK conditions. 31
conduct dosing experiments, as FFP (platelet-poor plasma)
and PRP differ in the concentration of the molecular pool Research focused on the integration of bioprinting,
released by platelets. cell therapies, and drug delivery has been recently
reviewed. To understand the potentiality of the biocarrier
32
The therapeutic potential of MSCs is well-recognized under investigation, the first challenge was to describe
due to their trophic actions and ability to modulate the complex pool of signaling proteins, followed by the
inflammation in the environment in which they are biological processes triggered upon in vivo implantation.
implanted. 26,27 BMSCs are the most commonly used source To address the former, we used arrays to quantify up to
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 311 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4426