Page 78 - IJB-7-1
P. 78
Using Plant Proteins to Develop Composite Scaffolds
A
B
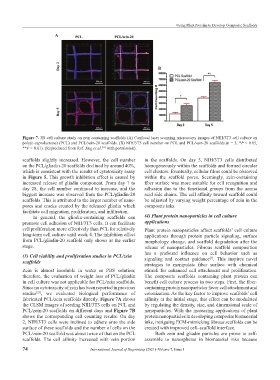
Figure 7. 3D cell culture study on zein containing scaffolds (A) Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of NIH/3T3 cell culture on
poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and PCL/zein-20 scaffolds. (B) NIH/3T3 cell number on PCL and PCL/zein-20 scaffolds.(n = 3, *P < 0.05,
**P < 0.01). (Reproduced from Ref. Jing et al. with permission).
[23]
scaffolds slightly increased. However, the cell number in the scaffolds. On day 5, NIH/3T3 cells distributed
on the PCL/gliadin-20 scaffolds declined by around 40%, homogeneously within the scaffolds and formed circular
which is consistent with the results of cytotoxicity assay cell clusters. Eventually, cellular films could be observed
in Figure 5. This growth inhibition effect is caused by within the scaffold pores. Seemingly, zein-containing
increased release of gliadin component. From day 7 to fiber surface was more suitable for cell recognition and
day 28, the cell number continued to increase, and the adhesion due to the functional groups from the amino
biggest increase was observed from the PCL/gliadin-20 acid side chains. The cell affinity toward scaffold could
scaffolds. This is attributed to the larger number of nano- be adjusted by varying weight percentage of zein in the
pores and cracks created by the released gliadin which composite inks.
facilitate cell migration, proliferation, and infiltration.
In general, the gliadin-containing scaffolds can (4) Plant protein nanoparticles in cell culture
promote cell adhesion of NIH/3T3 cells. It can facilitate applications
cell proliferation more effectively than PCL for relatively Plant protein nanoparticles affect scaffolds’ cell culture
long-term cell culture until week 4. The inhibition effect applications through protein particle signaling, surface
from PCL/gliadin-20 scaffold only shows at the earlier morphology change, and scaffold degradation after the
stage. release of nanoparticles. Fibrous scaffold composition
has a profound influence on cell behavior such as
(3) Cell viability and proliferation studies in PCL/zein signaling and contact guidance . This inspires novel
[1]
scaffolds
strategies to manipulate fiber surface with chemical
Zein is almost insoluble in water or PBS solution; stimuli for enhanced cell attachment and proliferation.
therefore, the evaluation of weight loss of PCL/gliadin The composite scaffolds containing plant protein can
in cell culture was not applicable for PCL/zein scaffolds. benefit cell culture process in two steps. First, the fiber-
Since no cytotoxicity of zein has been reported in previous containing protein nanoparticles favor cell attachment and
studies , we evaluated biological performance of colonization. As the key factor to improve scaffolds’ cell
[23]
fabricated PCL/zein scaffolds directly. Figure 7A shows affinity at the initial stage, this effect can be modulated
the CLSM images of seeding NIH/3T3 cells on PCL and by regulating the density, size, and dimensional scale of
PCL/zein-20 scaffolds on different days and Figure 7B nanoparticles. With the increasing applications of plant
shows the corresponding cell counting results. On day protein nanoparticles in developing composite biomaterial
2, NIH/3T3 cells were inclined to adhere onto the side inks, intriguing ECM-mimicking fibrous scaffolds can be
surface of these scaffolds and the number of cells on the created with improved cell–scaffold interface.
PCL/zein-20 scaffold was about twice of that on the PCL Both zein and gliadin particles are prone to self-
scaffolds. The cell affinity increased with zein portion assemble to nanospheres in biomaterial inks because
74 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 1