Page 97 - IJB-7-1
P. 97
Cunico
This also indicates that the cooling time enhanced two optical microscope Digital Avangard Optics AN-E500
types of heat treatment (quenching for fast cooling and (AVANGARD 2011), which a magnitude of up to ×500
annealing for slow cooling). Therefore, the effect of such of amplification. For the gravimetric analysis (drying
treatments on crystallization level, mechanical strength, monitoring), we used a 0.005 g error scale. To identify
and geometry distortion can be evidenced. On the other dimensional distortions of the specimen, we used both
hand, holding time and heating rate are expected to affect 0.05 mm caliper and computational image processing to
the sinterization parameters, such as nucleation, grain measure the specimen dimensions. After measuring, we
growth, and diffusion. used MATLAB software to perform statistical analysis
For the sintering process, we used a 2000 W and evidence the geometrical variation of object external
electrical Furnace PID controller with 4 ramps curves contour. To measure feasibility response, we established a
and insulation muffle. The main control parameters and scale from 0 to 1 in which level 1 indicates that the object
schematic sintering temperature curves that we applied in has no significant distortions and is feasible to be used;
this study are illustrated in Figure 2. level 0.75 exposes minor distortion which corresponds to
The flexural testing was performed in accordance 5% of distortion; and level 0.5 indicates that the object
with ISO 6872 in an EMIC DL10000 universal testing has 10% of distortion. It is important to note that the
machine. We used MATLAB software for the image measurement of feasibility response was used to analyze
processing, and the image acquisition was performed using non-volumetric distortions and compare CAD models
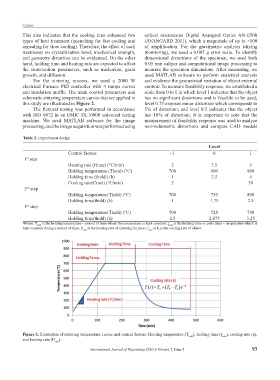
Table 2. Experiment design
Level
Control factors −1 0 1
1 step
st
Heating rate (Hrate) (°C/min) 2 3.5 5
Holding temperature (Thold) (°C) 700 800 900
Holding time (thold ) (h) 1 2.5 4
Cooling rate(Crate) (°C/min) 2 30
2 step
nd
Holding temperature(Thold) (°C) 700 750 800
Holding time(thold) (h) 1 1.75 2.5
3 step
rd
Holding temperature(Thold) (°C) 700 725 750
Holding time(thold) (h) 2.5 2.875 3.25
Where: T hold is the holding temperature – period of time where the temperature is kept constant; t hold is the holding time or plato time – temperature which is
kept constant during a period of time; H is the heating rate of sintering furnace; C or k is the cooling rate of object.
rate rate
Figure 2. Illustration of sintering temperature curves and control factors: Holding temperature (T hold ), holding time (t hold ), cooling rate (k),
and heating rate (H ).
rate
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 1 93