Page 77 - IJB-7-2
P. 77
González, et al.
Kidney is the most in-demand organ, but it is also A Other
a very defiant organ to mimic due to its sophisticated 2%
physiological architecture of multiple different cell Laser Based
types. In addition, this organ is solid (not hollow), 8%
making the task of bioprinting an artificial kidney very
challenging . Not surprisingly, only 1% of the retrieved Droplet Based
[72]
14%
articles addressed the bioprinting of kidney tissues [73,74] . Extrusion Based
76%
4. Bioinks for different bioprinting
technologies
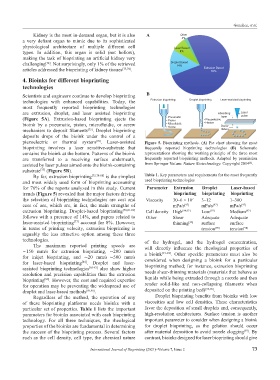
Scientists and engineers continue to develop bioprinting B
technologies with enhanced capabilities. Today, the Extrusion bioprinting Droplet bioprinting Laser-assisted bioprinting
most frequently reported bioprinting technologies
are extrusion, droplet, and laser assisted bioprinting Absorbing Laser
pulse
(Figure 5A). Extrusion-based bioprinting ejects the • Pneumatic • Piezoelectric layer
• Piston
bioink by a pneumatic, piston, microfluidic, or screw • Microfluidic • Heater Donor
• Screw
mechanism to deposit filaments . Droplet bioprinting ribbon
[75]
deposits drops of the bioink under the control of a
piezoelectric or thermal system . Laser-assisted Figure 5. Bioprinting methods. (A) Pie chart showing the most
[76]
bioprinting involves a laser sensitive-substrate that frequently reported bioprinting technologies (B) Schematic
contains the bioink at the bottom. Patterns of the bioink representations showing the working principle of the three most
are transferred to a receiving surface underneath, frequently reported bioprinting methods. Adapted by permission
[6]
assisted by laser pulses aimed onto the bioink-containing from Springer Nature: Nature Biotechnology. Copyright 2014 .
substrate (Figure 5B).
[77]
By far, extrusion bioprinting [75,78-80] is the simplest Table 1. Key parameters and requirements for the most frequently
and most widely used form of bioprinting accounting used bioprinting technologies
for 76% of the reports analyzed in this study. Current Parameter Extrusion Droplet Laser‑based
trends (Figure 5) revealed that the major factors driving bioprinting bioprinting bioprinting
the selection of bioprinting technologies are cost and Viscosity 30–6 × 10 3–12 1–300
7
ease of use, which are, in fact, the main strengths of mPa/s [97] mPa/s [97] mPa/s [97]
extrusion bioprinting. Droplet-based bioprinting [76,81-83] Cell density High [94,97] Low [97] Medium [97]
follows with a presence of 14%, and papers related to Other Shear Adequate Adequate
laser-assisted bioprinting [77] account for 8%. However, thinning [98] surface surface
in terms of printing velocity, extrusion bioprinting is tension [98] tension [98]
arguably the less attractive option among these three
technologies. of the hydrogel, and the hydrogel concentration,
The maximum reported printing speeds are will directly influence the rheological properties of
~150 mm/s for extrusion bioprinting, ~200 mm/s a bioink [91-94] . Other specific parameters must also be
for inkjet bioprinting, and ~20 mm/s–~500 mm/s considered when designing a bioink for a particular
for laser-based bioprinting . Droplet and laser-
[84]
assisted bioprinting technologies [85-87] also show higher bioprinting method; for instance, extrusion bioprinting
resolution and precision capabilities than the extrusion needs shear-thinning materials (materials that behave as
bioprinting . However, the cost and required expertise liquids while being extruded through a nozzle and then
[88]
for operation may be preventing the widespread use of render solid-like and non-collapsing filaments when
droplet and laser-based methods [89,90] . deposited on the printing bed) [95,96] .
Regardless of the method, the operation of any Droplet bioprinting benefits from bioinks with low
of these bioprinting platforms needs bioinks with a viscosities and low cell densities. These characteristics
particular set of properties. Table 1 lists the important favor the deposition of small droplets and, consequently,
parameters for bioinks associated with each bioprinting high-resolution architectures. Surface tension is another
technology. For all three techniques, the rheological important parameter to consider when designing a bioink
properties of the bioinks are fundamental in determining for droplet bioprinting, as the gelation should occur
the success of the bioprinting process. Several factors after material deposition to avoid nozzle clogging . By
[97]
such as the cell density, cell type, the chemical nature contrast, bioinks designed for laser bioprinting should give
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2 73