Page 80 - IJB-7-2
P. 80
A Scientometric Analysis
A B
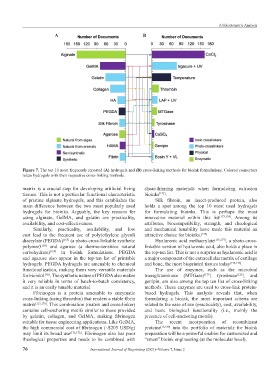
Figure 7. The top 10 most frequently reported (A) hydrogels and (B) cross-linking methods for bioink formulations. Colored connectors
relate hydrogels with their respective cross-linking methods.
matrix is a crucial step for developing artificial living shear-thinning materials when formulating extrusion
tissues. This is not a particular functional characteristic bioinks [172] .
of pristine alginate hydrogels, and this establishes the Silk fibroin, an insect-produced protein, also
main difference between the two most popularly used holds a spot among the top 10 most used hydrogels
hydrogels for bioinks. Arguably, the key reasons for for formulating bioinks. This is perhaps the most
using alginate, GelMA, and gelatin are practicality, innovative material within this list [173,174] . Among its
availability, and cost-effectiveness. attributes, biocompatibility, strength, and rheological
Similarly, practicality, availability, and low and mechanical tunability have made this material an
cost lead to the frequent use of poly(ethylene glycol) attractive choice for bioinks. [175]
diacrylate (PEGDA) [167] (a photo-cross-linkable synthetic Hyaluronic acid methacrylate [176,177] , a photo-cross-
polymer) [168] and agarose (a thermo-sensitive natural linkable version of hyaluronic acid, also holds a place in
carbohydrate) [169] in bioink formulations. PEGDA the top-ten list. This is not a surprise as hyaluronic acid is
and agarose also appear in the top-ten list of printable a major component of the extracellular matrix of cartilage
hydrogels. PEGDA hydrogels are amenable to chemical and bone, the most bioprinted tissues today [177,178] .
functionalization, making them very versatile materials The use of enzymes, such as the microbial
for bioinks [168] . The synthetic nature of PEGDA also makes transglutaminase (MTGase) [179] , tyrosinase [128] , and
it very reliable in terms of batch-to-batch consistency, genipin, are also among the top ten list of cross-linking
and it is an easily tunable material. methods. These enzymes are used to cross-link protein-
Fibrinogen is a protein amenable to enzymatic based hydrogels. This analysis reveals that, when
cross-linking (using thrombin) that renders a stable fibrin formulating a bioink, the most important criteria are
matrix [113,170] . This combination (matrix and cross-linker) related to the ease of use (practicality), cost, availability,
contains cell-anchoring motifs similar to those provided and basic biological functionality (i.e., mainly the
by gelatin, collagen, and GelMA, making fibrinogen presence of cell-anchoring motifs).
suitable for tissue engineering applications. Like GelMA, The recent incorporation of recombinant
the high commercial cost of fibrinogen (~$205 USD/g) proteins [18,180] into the portfolio of materials for bioink
may limit its broad use [171,172] . Fibrinogen also has poor preparation will be a powerful enabler for customized and
rheological properties and needs to be combined with “smart” bioink engineering (at the molecular level).
76 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2