Page 8 - IJB-7-2
P. 8
The Role of 3DP Phantoms and Devices for Organ-specified Appliances in Urology
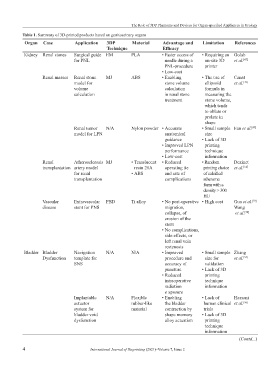
Table 1. Summary of 3D-printed products based on genitourinary organs
Organ Case Application 3DP Material Advantage and Limitation References
Technique Efficacy
Kidney Renal stones Surgical guide EM PLA • Faster access of • Requiring an Golab
for PNL needle during a on-site 3D et al. [47]
PNL-procedure printer
• Low-cost
Renal masses Renal stone MJ ABS • Enabling • The use of Canat
model for stone volume ellipsoid et al. [39]
volume calculation formula in
calculation in renal stone measuring the
treatment stone volume,
which tends
to oblate or
prolate in
shape
Renal tumor N/A Nylon powder • Accurate • Small sample Fan et al. [49]
model for LPN anatomical size
guidance • Lack of 3D
• Improved LPN printing
performance technique
• Low-cost information
Renal Atherosclerosis MJ • Translucent • Reduced • Random Dezinet
transplantation artery model resin 28A operating tie printing choice et al. [52]
for renal • ABS and rate of of calcified
transplantation complications atheroma
form with a
density > 300
HU
Vascular Extravascular PBD Ti alloy • No post-operative • High cost Guo et al. [54]
disease stent for PNS migration, Wang
collapse, of et al. [54]
erosion of the
stent
• No complications,
side effects, or
left renal vein
restenosis
Bladder Bladder Navigation N/A N/A • Improved • Small sample Zhang
Dysfunction template for procedure and size for et al. [55]
SNS accuracy of validation
puncture • Lack of 3D
• Reduced printing
intraoperative technique
radiation information
e xposure
Implantable N/A Flexible • Enabling • Lack of Hassani
actuator rubber-like the bladder human clinical et al. [56]
system for material contraction by trials
bladder void shape memory • Lack of 3D
dysfunction alloy actuation printing
technique
information
(Contd...)
4 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2