Page 14 - IJB-8-2
P. 14
Electrohydrodynamic Printed Sub-microscale Fibrous Architectures Improved Cell Attachment and Collagen Type I Deposition
A B C
G
D E F
H
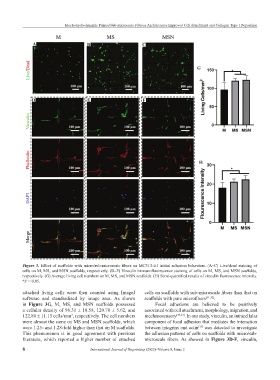
Figure 3. Effect of scaffolds with micro/sub-microscale fibers on MC3T3-E1 initial adhesion behaviors. (A–C) Live/dead staining of
cells on M, MS, and MSN scaffolds, respectively. (D–F) Vinculin immunofluorescence staining of cells on M, MS, and MSN scaffolds,
respectively. (G) Average living cell numbers on M, MS, and MSN scaffolds. (H) Semi-quantified results of vinculin fluorescence intensity.
*P < 0.05.
attached living cells were then counted using ImageJ cells on scaffolds with sub-microscale fibers than that on
software and standardized by image area. As shown scaffolds with pure microfibers [31,32] .
in Figure 3G, M, MS, and MSN scaffolds possessed Focal adhesions are believed to be positively
a cellular density of 96.31 ± 18.58, 120.70 ± 5.62, and associated with cell attachment, morphology, migration, and
122.80 ± 11.15 cells/mm , respectively. The cell numbers mechanosensory [33,34] . In our study, vinculin, an intracellular
2
were almost the same on MS and MSN scaffolds, which component of focal adhesion that mediates the interaction
were 1.25- and 1.28-fold higher than that on M scaffolds. between integrins and actin was detected to investigate
[35]
This phenomenon is in good agreement with previous the adhesion patterns of cells on scaffolds with micro/sub-
literature, which reported a higher number of attached microscale fibers. As showed in Figure 3D-F, vinculin,
6 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2