Page 17 - IJB-8-2
P. 17
Hu, et al.
in MSN scaffolds (Figure 5C, F and I). These results phosphate ions, which plays an essential role in the
[39]
evidenced that the scaffolds with sub-microscale fibers formation of hydroxyapatite crystals of bone matrices .
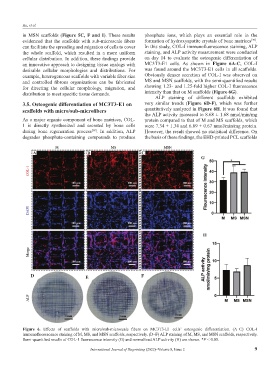
can facilitate the spreading and migration of cells to cover In this study, COL-I immunofluorescence staining, ALP
the whole scaffold, which resulted in a more uniform staining, and ALP activity measurement were conducted
cellular distribution. In addition, these findings provide on day 14 to evaluate the osteogenic differentiation of
an innovative approach to designing tissue analogs with MC3T3-E1 cells. As shown in Figure 6A-C, COL-I
desirable cellular morphologies and distributions. For was found around the MC3T3-E1 cells in all scaffolds.
example, heterogeneous scaffolds with variable fiber size Obviously denser secretion of COL-I was observed on
and controlled fibrous organizations can be fabricated MS and MSN scaffolds, with the semi-quantified results
for directing the cellular morphology, migration, and showing 1.23- and 1.25-fold higher COL-I fluorescence
distribution to meet specific tissue demands. intensity than that on M scaffolds (Figure 6G).
ALP staining of different scaffolds exhibited
3.5. Osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 on very similar trends (Figure 6D-F), which was further
scaffolds with micro/sub-microfibers quantitatively analyzed in Figure 6H. It was found that
the ALP activity increased to 8.68 ± 1.68 nmol/min/mg
As a major organic component of bone matrices, COL- protein compared to that of M and MS scaffolds, which
1 is directly synthesized and secreted by bone cells were 7.34 ± 1.34 and 6.89 ± 0.67 nmol/min/mg protein.
during bone regeneration process . In addition, ALP However, the result showed no statistical difference. On
[38]
degrades phosphate-containing compounds to produce the basis of these findings, the EHD-printed PCL scaffolds
A B C
G
H
D E F
Figure 6. Effects of scaffolds with micro/sub-microscale fibers on MC3T3-E1 cells’ osteogenic differentiation. (A–C) COL-I
immunofluorescence staining of M, MS, and MSN scaffolds, respectively. (D–F) ALP staining of M, MS, and MSN scaffolds, respectively.
Semi-quantified results of COL-1 fluorescence intensity (G) and normalized ALP activity (H) are shown. *P < 0.05.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 9