Page 140 - IJB-8-2
P. 140
3D Printing of Hollow Microneedle Patches
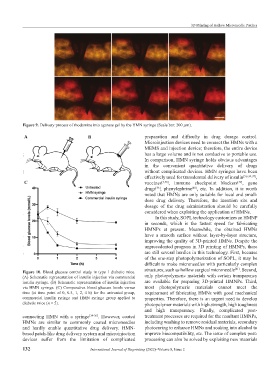
Figure 9. Delivery process of rhodamine into agarose gel by the HMN syringe (Scale bar: 200 μm).
A B preparation and difficulty in drug dosage control.
Microinjection devices need to connect the HMNs with a
MEMS and injection device; therefore, the entire device
has a large volume and is not conducive to portable use.
In comparison, HMN syringe holds obvious advantages
in the convenient quantitative delivery of drugs
without complicated devices. HMN syringes have been
effectively used for transdermal delivery of insulin [5,6,34,37] ,
C vaccines [7,38] , immune checkpoint blockers , gene
[39]
drugs , phenylephrine , etc. In addition, it is worth
[36]
[40]
noted that HMNs are only suitable for local and small-
dose drug delivery. Therefore, the insertion site and
dosage of the drug administration should be carefully
considered when exploiting the application of HMNs.
In this study, SOPL technology customizes an HMNP
in seconds, which is the fastest speed for fabricating
HMNPs at present. Meanwhile, the obtained HMNs
have a smooth surface without layer-by-layer structure,
improving the quality of 3D-printed HMNs. Despite the
unprecedented progress in 3D printing of HMNPs, there
are still several hurdles in this technology. First, because
of the one-step photopolymerization of SOPL, it may be
difficult to make microneedles with particularly complex
structures, such as hollow surgical microneedle . Second,
[41]
Figure 10. Blood glucose control study in type 1 diabetic mice.
(A) Schematic representation of insulin injection via commercial only photopolymeric materials with certain transparency
insulin syringe. (B) Schematic representation of insulin injection are available for preparing 3D-printed HMNPs. Third,
via HMN syringe. (C) Comparative blood glucose levels versus most photopolymeric materials cannot meet the
time (at time point of 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 h) for the untreated group, requirement of fabricating HMNs with good mechanical
commercial insulin syringe and HMN syringe group applied to properties. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop
diabetic mice (n = 5). photopolymer materials with high strength, high toughness
and high transparency. Finally, complicated post-
connecting HMN with a syringe [34-36] . However, coated treatment processes are required for the resultant HMNPs,
HMNs are similar to commonly coated microneedles including washing to remove residual materials, secondary
and hardly enable quantitative drug delivery. HMN- photocuring to enhance HMNs and soaking into alcohol to
based patch-like drug delivery system and microinjection improve biocompatibility, etc. The issue of complex post-
devices suffer from the limitation of complicated processing can also be solved by exploiting new materials
132 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2