Page 48 - IJB-8-2
P. 48
3D-Printed β-TCP scaffolds promote Osteogenic Differentiation of BMSCs in an m6A-Dependent Manner
A B C
D F
E
G H
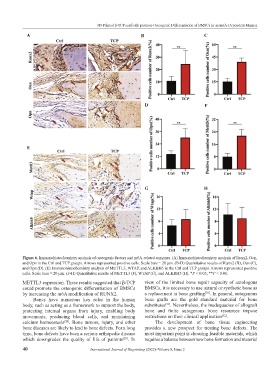
Figure 6. Immunohistochemistry analysis of osteogenic factors and m6A-related enzymes. (A) Immunohistochemistry analysis of Runx2, Ocn,
and Opn in the Ctrl and TCP groups. Arrows represented positive cells. Scale bars = 20 μm. (B-D) Quantitative results of Runx2 (B), Ocn (C),
and Opn (D). (E) Immunohistochemistry analysis of METTL3, WTAP, and ALKBH5 in the Ctrl and TCP groups. Arrows represented positive
cells. Scale bars = 20 μm. (F-H) Quantitative results of METTL3 (F), WTAP (G), and ALKBH5 (H). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
METTL3 expression. These results suggested that β-TCP view of the limited bone repair capacity of autologous
could promote the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs BMSCs, it is necessary to use natural or synthetic bone as
by increasing the m6A modification of RUNX2. a replacement in bone grafting . In general, autogenous
[30]
Bones have numerous key roles in the human bone grafts are the gold standard material for bone
body, such as acting as a framework to support the body, substitutes . Nevertheless, the inadequacies of allograft
[31]
protecting internal organs from injury, enabling body bone and finite autogenous bone resources impose
movements, producing blood cells, and maintaining restrictions on their clinical application .
[32]
calcium homeostasis . Bone tumors, injury, and other The development of bone tissue engineering
[28]
bone diseases are likely to lead to bone defects. For a long provides a new prospect for treating bone defects. The
time, bone defects have been a serious orthopedic disease most important point is choosing feasible materials, which
which downgrades the quality of life of patients . In requires a balance between new bone formation and material
[29]
40 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2