Page 49 - IJB-8-2
P. 49
Jiao, et al.
The mechanism by which β-TCP contributes to
osteogenesis is not well understood. To begin with
investigating the mechanism, we note that the m6A
modification shows strong association with osteogenesis,
and METTL3 affects the osteogenic differentiation of
BMSCs through the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and the
expression level of VEGF . In C3H10T1/2 cells, FTO
[41]
and p-AMPK form a positive feedback loop, stimulating
endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and inducing
osteogenic differentiation . In view of the above, we
[42]
investigated the mechanism by which β-TCP contributed
to osteogenesis in terms of m6A modification. It was found
that mRNA and protein levels of METTL3 both increased
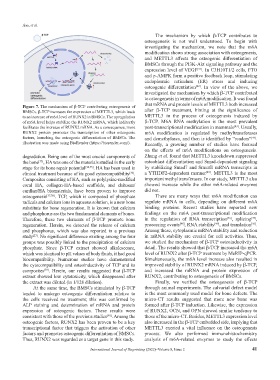
Figure 7. The mechanism of β-TCP contributing osteogenesis of
BMSCs. β-TCP increases the expression of METTL3, which leads after β-TCP treatment, hinting at the significance of
to an increase of m6A level of RUNX2 in BMSCs. The upregulation METTL3 in the process of osteogenesis induced by
of m6A level helps stabilize the RUNX2 mRNA, which indirectly β-TCP. M6A RNA methylation is the most prevalent
[43]
facilitates the increase of RUNX2 mRNA. As a consequence, more post-transcriptional modification in mammals . Usually,
RUNX2 protein promotes the transcription of other osteogenic m6A modification is regulated by methyltransferases
factors, launching the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. The and demethylases, and then is identified by “readers” .
[44]
illustration was made using BioRender (https://biorender.com/). Recently, a growing number of studies have focused
on the effects of m6A modifications on osteogenesis.
degradation. Being one of the most crucial components of Zhang et al. found that METTL3 knockdown suppressed
the bone , HA was one of the materials studied in the early osteoblast differentiation and Smad-dependent signaling
[33]
stage for its bone repair potential [34,35] . HA has been used in by stabilizing Smad7 and Smurf1 mRNA transcripts in
[45]
clinical treatment because of its good cytocompatibility . a YTHDF2-dependent manner . METTL3 is the most
[36]
Composites consisting of HA, such as polylysine-modified important methyltransferases. In our study, METTL3 also
coral HA, collagen-HA-based scaffolds, and chitosan/ showed increase while the other m6A-related enzymes
curdlan/HA biomaterials, have been proven to improve did not.
osteogenesis [37,38] . TCP, which is composed of phosphate There are many ways that m6A modification can
radicals and calcium ions in aqueous solution, is a new bone regulate mRNA in cells, depending on different m6A
substitute for bone regeneration. It is known that calcium binding proteins. Recent studies have reported new
and phosphorus are the two fundamental elements of bones. findings on the m6A post-transcriptional modification
Therefore, these two elements of β-TCP promote bone in the regulation of RNA transcription , splicing ,
[47]
[46]
[50]
regeneration. Herein, we detected the release of calcium processing events , RNA stability , and translation .
[48]
[49]
and phosphorus, which was also reported in a previous Among these, cytoplasmic mRNA stability and reduction
study . No significant difference existing among the four in mRNA stability are crucial for cell activities. Thus,
[27]
groups was possibly linked to the precipitation of calcium we studied the mechanism of β-TCP osteoinductivity in
phosphate. Since β-TCP extract showed alkalescence, detail. The results showed that β-TCP increased the m6A
which was identical to pH values of body fluids, it had good level of RUNX2 after β-TCP treatment by MeRIP-qPCR.
biocompatibility. Numerous studies have demonstrated Simultaneously, the m6A level increase also resulted in
the cytocompatibility and osteoinductivity of TCP and its improved stability of RUNX2 mRNA induced by β-TCP,
composites . Herein, our results suggested that β-TCP and increased the mRNA and protein expression of
[39]
extract showed low cytotoxicity, which disappeared after RUNX2, contributing to osteogenesis of BMSCs.
the extract was diluted (in 1/128 dilution). Finally, we verified the osteogenesis of β-TCP
At the same time, the BMSCs stimulated by β-TCP through animal experiments. The calvarial defect model
tended to undergo osteogenic differentiation relative to is the most commonly used model for bone defects. The
the cells received no treatment; this was confirmed by micro-CT results suggested that more new bone was
ALP staining and determination of mRNA and protein formed after β-TCP induction. Likewise, the expression
expression of osteogenic factors. These results were of RUNX2, OCN, and OPN showed similar tendency to
consistent with those of the previous studies . Among the those of the micro-CT. Besides, METTL3 expression level
[40]
osteogenic factors, RUNX2 has been proven to be a key also increased in the β-TCP embedded side, implying that
transcriptional factor that triggers the activation of other METTL3 exerted a vital influence on the osteogenesis
factors and promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. process. We also performed immunohistochemistry
Thus, RUNX2 was regarded as a target gene in this study. analysis of m6A-related enzymes to study the effects
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 41