Page 170 - IJB-9-1
P. 170
International Journal of Bioprinting Lumen-forming colorectal cancer organoids
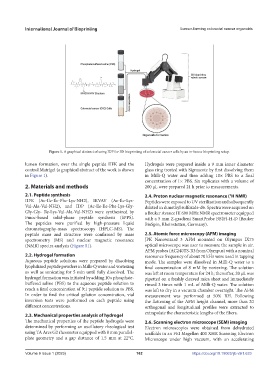
Figure 1. A graphical abstract of using IDP for 3D bioprinting of colorectal cancer cells by an in-house bioprinting setup.
lumen formation, over the single peptide IIFK and the Hydrogels were prepared inside a 9 mm inner diameter
control Matrigel (a graphical abstract of the work is shown glass ring treated with Sigmacote by first dissolving them
in Figure 1). in Milli-Q water and then adding 10× PBS to a final
concentration of 1× PBS. Six replicates with a volume of
2. Materials and methods 200 µL were prepared 21 h prior to measurements.
2.1. Peptide synthesis 2.4. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance ( H NMR)
1
IIFK (Ac-Ile-Ile-Phe-Lys-NH2), IKVAV (Ac-Ile-Lys- Peptides were exposed to UV sterilization and subsequently
Val-Ala-Val-NH2), and IDP (Ac-Ile-Ile-Phe-Lys-Gly- diluted in dimethyl sulfoxide-d6. Spectra were acquired on
Gly-Gly- Ile-Lys-Val-Ala-Val-NH2) were synthesized by a Bruker Avance III 600 MHz NMR spectrometer equipped
Fmoc-based solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). with a 5 mm Z-gradient SmartProbe BB(F)-H-D (Bruker
The peptides were purified by high-pressure liquid BioSpin, Rheinstetten, Germany).
chromatography-mass spectroscopy (HPLC-MS). The
peptide mass and structure were confirmed by mass 2.5. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) imaging
spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance JPK Nanowizard 3 AFM mounted on Olympus IX73
(NMR) spectra analysis (Figure S1). optical microscope was user to measure the sample in air.
AFM probes (AC240TS-R3 from Olympus) with a nominal
2.2. Hydrogel formation resonance frequency of about 70 kHz were used in tapping
Aqueous peptide solutions were prepared by dissolving mode. The samples were dissolved in Milli-Q water to a
lyophilized peptide powders in Milli-Q water and vortexing final concentration of 8 mM by vortexing. The solution
as well as sonicating for 5 min until fully dissolved. The was left at room temperature for 24 h; thereafter, 20 µL was
hydrogel formation was initiated by adding 10× phosphate- pipetted on a freshly cleaved mica sheet and immediately
buffered saline (PBS) to the aqueous peptide solution to rinsed 3 times with 1 mL of Milli-Q water. The solution
reach a final concentration of 9:1 peptide solution to PBS. was left to dry in a vacuum chamber overnight. The AFM
In order to find the critical gelation concentration, vial measurement was performed at 50% RH. Following
inversion tests were performed on each peptide using the flattening of the AFM height channel, more than 20
different concentrations. orthogonal and longitudinal profiles were extracted to
extrapolate the characteristic lengths of the fibers.
2.3. Mechanical properties analysis of hydrogel
The mechanical properties of the peptide hydrogels were 2.6. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) imaging
determined by performing an oscillatory rheological test Electron microscopies were obtained from dehydrated
using TA Ares G2 rheometer equipped with 8 mm parallel- scaffolds in an FEI Magellan 400 XHR Scanning Electron
plate geometry and a gap distance of 1.5 mm at 22°C. Microscope under high vacuum, with an accelerating
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 162 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.633
V