Page 46 - IJB-9-1
P. 46
International Journal of Bioprinting Effect of ionic crosslinking on composite membranes
solution (3 wt %) for 2 h. The resulting supercritical fluids- 2.5. Instruments
decellularized dermal-based sample was washed with FTIR was determined with a spectrometer (Nicolet IS10,
double-distilled water under ultrasonic wave, frozen for 6 h, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), and the data were collected
and then lyophilized (EYELA and FD-5N) at −45°C and 0.1 from 400 to 4000 cm . Morphology was studied by SEM
−1
[23]
– 0.2 torr. A kind of SFDDS was obtained . (S3400N, Hitachi, Japan). Thermal analysis was performed
by TGA using a thermoanalyzer (7300TG/DTA, Seiko,
2.3. Preparation of alginate-based composite Japan).
bioscaffolds containing ALG and SFDDS
First, the desired amount of SFDDS bioscaffold was added 3. Results and discussion
and dispersed completely in 40 mL of double-distilled water In this study, the SFDDS was prepared and identified by
to obtain dispersed SFDDS solution. Then, aqueous sodium collagen. The ScCO decellularization significantly reduced
2
alginate solution was homogenized thoroughly with the treatment times, achieved complete decellularization, and
dispersed SFDDS solution at 26,000 rpm for 3 min to obtain an
aqueous ALG/SFDDS solution. Further, the resulting aqueous A
ALG/SFDDS solution was molded and lyophilized at a freeze-
drying temperature of −45°C and pressure of 0.1 – 0.2 torr
overnight. A series of alginate-based composite bioscaffolds
with SFDDS bioscaffolds were obtained based on the various
ratios of sodium alginate and SFDDS (ALG/SFDDS: 80/20,
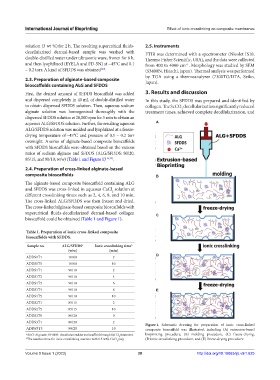
85/15, and 90/10; w/w) (Table 1 and Figure 1) [15,24] .
2.4. Preparation of cross-linked alginate-based
composite bioscaffolds B
The alginate-based composite bioscaffold containing ALG
and SFDDS was cross-linked in aqueous CaCl solution at
2
different crosslinking times such as 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 min.
The cross-linked ALG/SFDDS was then frozen and dried.
The cross-linked alginate-based composite bioscaffolds with
supercritical fluids-decellularized dermal-based collagen C
bioscaffold could be obtained (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Table 1. Preparation of ionic cross-linked composite
bioscaffolds with SFDDS.
Sample no. ALG/SFDDS a Ionic crosslinking time b
(w/w) (min)
D
ADDS0T1 100/0 2
ADDS0T5 100/0 10
ADDS1T1 90/10 2
ADDS1T2 90/10 4
ADDS1T3 90/10 6
ADDS1T4 90/10 8 E
ADDS1T5 90/10 10
ADDS2T1 85/15 2
ADDS2T5 85/15 10
ADDS3T0 80/20 0
ADDS3T1 80/20 2 Figure 1. Schematic drawing for preparation of ionic cross-linked
ADDS3T5 80/20 10 composite bioscaffold was illustrated, including (A) extrusion-based
a ALG: Alginate; SFDDS: Decellularized dermal scaffold through ScCO treatment. bioprinting procedure, (B) molding procedure, (C) freeze-drying,
2
b The reaction time for ionic crosslinking reaction with 0.5 wt% CaCl (aq) . (D ionic crosslinking procedure, and (E) freeze-drying procedure.
2
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 38 http://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.625