Page 310 - IJB-9-2
P. 310
International Journal of Bioprinting Zn-doped coatings with osteogenic and antibacterial properties
A
B
C D E F
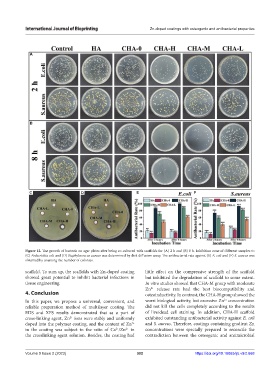
Figure 12. The growth of bacteria on agar plates after being co-cultured with scaffolds for (A) 2 h and (B) 8 h. Inhibition zone of different samples to
(C) Escherichia coli and (D) Staphylococcus aureus was determined by disk diffusion assay. The antibacterial rate against (E) E. coli and (F) S. aureus was
obtained by counting the number of colonies.
scaffold. To sum up, the scaffolds with Zn-doped coating little effect on the compressive strength of the scaffold
showed great potential to inhibit bacterial infections in but inhibited the degradation of scaffold to some extent.
tissue engineering. In vitro studies showed that CHA-M group with moderate
2+
Zn release rate had the best biocompatibility and
4. Conclusion osteoinductivity. In contrast, the CHA-H group showed the
2+
In this paper, we propose a universal, convenient, and worst biological activity, but excessive Zn concentration
reliable preparation method of multilayer coating. The did not kill the cells completely according to the results
EDS and XPS results demonstrated that as a part of of live/dead cell staining. In addition, CHA-H scaffold
cross-linking agent, Zn ions were stably and uniformly exhibited outstanding antibacterial activity against E. coli
2+
doped into the polymer coating, and the content of Zn and S. aureus. Therefore, coatings containing gradient Zn
2+
in the coating was subject to the ratio of Ca /Zn in concentrations were specially prepared to reconcile the
2+
2+
the crosslinking agent solution. Besides, the coating had contradiction between the osteogenic and antimicrobial
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 302 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.668