Page 308 - IJB-9-2
P. 308
International Journal of Bioprinting Zn-doped coatings with osteogenic and antibacterial properties
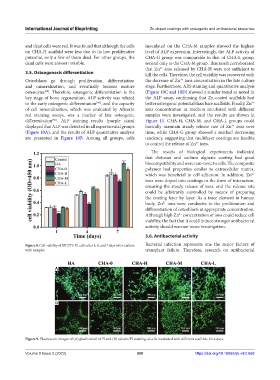
and dead cells were red. It was found that although the cells inoculated on the CHA-M samples showed the highest
on CHA-H scaffold were less due to its low proliferative level of ALP expression. Interestingly, the ALP activity of
potential, only a few of them died. For other groups, the CHA-G group was comparable to that of CHA-L group,
dead cells were almost invisible. second only to the CHA-M group. This result corroborated
that Zn ions released by CHA-H were not sufficient to
2+
3.5. Osteogenesis differentiation kill the cells. Therefore, the cell viability was recovered with
2+
Osteoblasts go through proliferation, differentiation the decrease of Zn ions concentration in the late culture
and mineralization, and eventually become mature stage. Furthermore, ARS staining and quantitative analysis
osteocytes . Therefore, osteogenic differentiation is the (Figure 10C and 10D) showed a similar trend as noted in
[48]
key stage of bone regeneration. ALP activity was related the ALP assay, confirming that Zn-coated scaffolds had
to the early osteogenic differentiation , and the capacity better osteogenic potential than bare scaffolds. Finally, Zn
2+
[49]
of cell mineralization, which was evaluated by Alizarin ions concentration in medium incubated with different
red staining assays, was a marker of late osteogenic samples were investigated, and the results are shown in
differentiation . ALP staining results (purple stain) Figure 11. CHA-H, CHA-M, and CHA-L groups could
[50]
displayed that ALP was detected in all experimental groups basically maintain steady release rate of Zn ions over
2+
(Figure 10A), and the results of ALP quantitative analysis time, while CHA-G group showed a marked decreasing
are presented in Figure 10B. Among all groups, cells tendency, suggesting that multilayer coatings are feasible
to control the release of Zn ions.
2+
The results of biological experiments indicated
that chitosan and sodium alginate coating had good
biocompatibility and were non-toxic to cells. The composite
polymer had properties similar to extracellular matrix,
which was beneficial to cell adhesion. In addition, Zn
2+
ions were doped into coatings in the form of interaction,
ensuring the steady release of ions, and the release rate
could be arbitrarily controlled by means of preparing
the coating layer by layer. As a trace element in human
body, Zn ions were conducive to the proliferation and
2+
differentiation of osteoblasts at appropriate concentration.
Although high Zn concentration of ions could reduce cell
2+
viability, the fact that it could induce stronger antibacterial
activity should warrant more investigation.
3.6. Antibacterial activity
Figure 8. Cell viability of MC3T3-E1 cells after 1, 4, and 7 days of co-culture Bacterial infection represents one the major factors of
with samples. transplant failure. Therefore, research on antibacterial
A
B
Figure 9. Fluorescent images of (A) phalloidin/DAPI and (B) calcein/PI staining of cells incubated with different scaffolds for 4 days.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 300 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.668