Page 421 - IJB-9-2
P. 421
International Journal of Bioprinting Design and 3D printing of TPMS breast scaffolds
3. Results and discussion are located on the vertical struts and the transverse struts
are low-stress areas, showing stripped patterns. The
3.1. Design and FEA of the TPMS scaffold high-stress areas of I-WP are mainly concentrated in the
Four TPMS scaffolds including Gyroid, Diamond, I-WP, narrow neck of the scaffold, and the areas are transversely
and Primitive were successfully designed in this study. banded. The location of the high-stress distribution areas
To explore the mechanical properties and permeability of in the Primitive scaffold are similar to that of the I-WP,
these scaffolds, the compression model and permeability which are concentrated in the structure neck. However,
model were established as described previously. The the shapes of high-stress areas in Primitive scaffold are
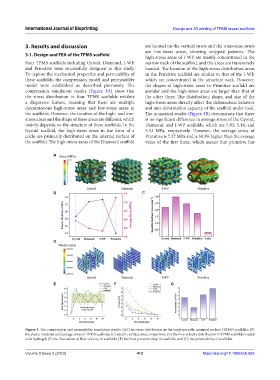
compression simulation results (Figure 3A) show that annular and the high-stress areas are larger than that of
the stress distribution in four TPMS scaffolds exhibits the other three. The distribution, shape, and size of the
a dispersive feature, meaning that there are multiple high-stress areas directly affect the deformation behavior
discontinuous high-stress areas and low-stress areas in and anti-deformation capacity of the scaffold under load.
the scaffolds. However, the location of the high- and low- The numerical results (Figure 3B) demonstrate that there
stress areas and the shape of these areas are different, which is no significant difference in average stress of the Gyroid,
mainly depends on the structure of these scaffolds. In the Diamond, and I-WP scaffolds, which are 5.93, 5.48, and
Gyroid scaffold, the high-stress areas in the form of a 5.33 MPa, respectively. However, the average stress of
circle are primarily distributed on the internal surface of Primitive is 7.27 MPa and is 30.3% higher than the average
the scaffold. The high-stress areas of the Diamond scaffold value of the first three, which means that primitive has
A
B C
D
E F G
Figure 3. The compression and permeability simulation results: (A) The stress distribution in the triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) scaffolds; (B)
the elastic modulus and average stress of TPMS scaffolds; (C) specific surface area comparison; (D) the flow velocity distribution in TPMS scaffolds loaded
with hydrogel; (E) the fluctuation of flow velocity in scaffolds; (F) the fluid pressure drop in scaffolds; and (G) the permeability of scaffolds.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 413 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.685