Page 454 - IJB-9-2
P. 454
International Journal of Bioprinting Fabrication of 3D functional hydrogel for wound dressings
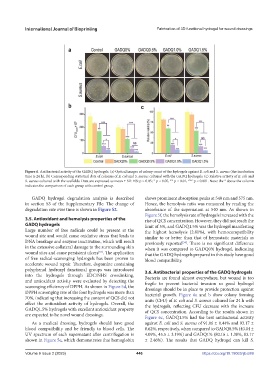
Figure 6. Antibacterial activity of the GADQ hydrogels. (a) Optical images of colony count of the hydrogels against E. coli and S. aureus (the incubation
time is 24 h). (b) Corresponding statistical data of colonies of E. coli and S. aureus cultured with the GADQ hydrogels. (c) Relative activity of E. coli and
S. aureus cultured with the scaffolds. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. NS: p > 0.05; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Note: the * above the column
indicates the comparison of each group with control group.
GADQ hydrogel degradation analysis is described shows prominent absorption peaks at 540 nm and 575 nm.
in section S3 of the Supplementary File. The change of Hence, the hemolysis ratio was measured by reading the
degradation rate over time is shown in Figure S2. absorbance of the supernatant at 540 nm. As shown in
Figure 5f, the hemolysis rate of hydrogels increased with the
3.5. Antioxidant and hemolysis properties of the rise of QCS concentration. However, they did not reach the
GADQ hydrogels limit of 5%, and GADQ1.5% was the hydrogel manifesting
Large number of free radicals could be present at the the highest hemolysis (2.81%), with hemocompatibility
wound site and would cause oxidative stress that leads to similar to or better than that of hemostatic materials as
DNA breakage and enzyme inactivation, which will result previously reported . There is no significant difference
[54]
in the extensive collateral damage to the surrounding skin when it was compared to GADQ0% hydrogel, indicating
wound sites and cause persistent ulcers . The application that the GADQ hydrogels prepared in this study have good
[53]
of free radical-scavenging hydrogels has been proven to blood compatibility.
accelerate wound repair. Therefore, dopamine containing
polyphenol hydroxyl functional groups was introduced 3.6. Antibacterial properties of the GADQ hydrogels
into the hydrogels through EDC/NHS crosslinking, Bacteria are found almost everywhere, but wound is too
and antioxidant activity were evaluated by detecting the fragile to prevent bacterial invasion so good hydrogel
scavenging efficiency of DPPH. As shown in Figure 5d, the dressings should be in place to provide protection against
DPPH scavenging rate of the four hydrogels was more than bacterial growth. Figure 6a and b show colony forming
70%, indicating that increasing the content of QCS did not units (CFU) of E. coli and S. aureus cultured for 24 h with
affect the antioxidant activity of hydrogels. Overall, the the hydrogels, reflecting CFU decrease with the increase
GADQ1.5% hydrogels with excellent antioxidant property of QCS concentration. According to the results shown in
are expected to be novel wound dressings.
Figure 6c, GADQ1.5% had the best antibacterial activity
As a medical dressing, hydrogels should have good against E. coli and S. aureus of 91.06 ± 0.44% and 93.17 ±
blood compatibility and be friendly to blood cells. The 0.62%, respectively, when compared to GADQ0.5% (40.04 ±
UV spectrum of each supernatant after centrifugation is 4.09%, 45.5 ± 3.19%) and GADQ1% (80.16 ± 1.38%, 83.17
shown in Figure 5e, which demonstrates that hemoglobin ± 2.46%). The results that GADQ hydrogel can kill S.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 446 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.689