Page 451 - IJB-9-2
P. 451
International Journal of Bioprinting Fabrication of 3D functional hydrogel for wound dressings
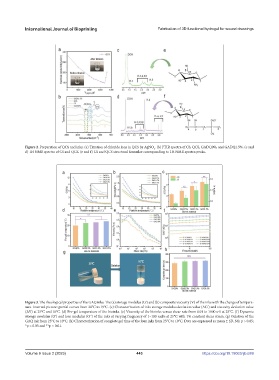
Figure 2. Preparation of QCS and inks. (a) Titration of chloride ions in QCS by AgNO . (b) FTIR spectra of CS, QCS, GADQ0%, and GADQ1.5%. (c and
3
d) 1H NMR spectra of CS and QCS. (e and f) CS and QCS structural formulae corresponding to 1H NMR spectra peaks.
Figure 3. The rheological properties of the GAQ inks. The (a) storage modulus (Gʹ) and (b) composite viscosity (V) of the inks with the change of tempera-
ture. Inserted picture: partial curves from 28°C to 19°C. (c) Characterization of inks storage modulus deviation value (∆Gʹ) and viscosity deviation value
(∆V) at 25°C and 10°C. (d) Pre-gel temperature of the bioinks. (e) Viscosity of the bioinks versus shear rate from 0.01 to 1000 s-1 at 25°C. (f) Dynamic
storage modulus (Gʹ) and loss modulus (G˝) of the inks at varying frequency of 1–100 rad/s at 25°C with 1% constant shear strain. (g) Gelation of the
GAQ ink from 25°C to 10°C. (h) Characterization of complete gel time of the four inks from 25°C to 10°C. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. NS: p > 0.05;
*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 443 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.689