Page 455 - IJB-9-2
P. 455
International Journal of Bioprinting Fabrication of 3D functional hydrogel for wound dressings
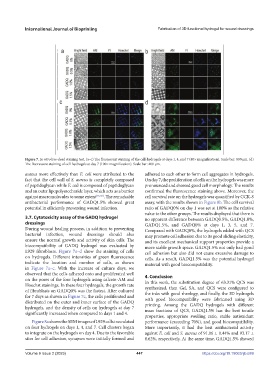
Figure 7. In vitro live-dead staining test. (a–c) The fluorescent staining of the cell-hydrogels at days 1, 4, and 7 (40× magnification). Scale bar: 800 μm. (d)
The fluorescent staining of cell-hydrogels at day 7 (100× magnification). Scale bar: 400 μm.
aureus more effectively than E. coli were attributed to the adhered to each other to form cell aggregates in hydrogels.
fact that the cell wall of S. aureus is completely composed On day 7, the proliferation of cells on the hydrogels was more
of peptidoglycan while E. coli is composed of peptidoglycan pronounced and showed good cell morphology. The results
and an outer lipopolysaccharide layer, which acts as a barrier confirmed the fluorescence staining above. Moreover, the
against macromolecules to some extent [55,56] . The remarkable cell survival rate on the hydrogels was quantified by CCK-8
antibacterial performance of GADQ1.5% showed great assay, with the results shown in Figure 8b. The cell survival
potential in efficiently preventing wound infection. ratio of GADQ0% on day 1 was set at 100% as the relative
value to the other groups. The results displayed that there is
3.7. Cytotoxicity assay of the GADQ hydrogel no apparent difference between GADQ0.5%, GADQ1.0%,
dressings GADQ1.5%, and GADQ0% at days 1, 3, 5, and 7.
During wound healing process, in addition to preventing Compared with GADQ0%, the hydrogels added with QCS
bacterial infection, wound dressings should also may promote cell adhesion due to its good sliding elasticity,
ensure the normal growth and activity of skin cells. The and its excellent mechanical support properties provide a
biocompatibility of GADQ hydrogel was evaluated by more stable growth space. GADQ1.5% not only had good
L929 fibroblasts. Figure 7a–d show the staining of cells cell adhesion but also did not cause excessive damage to
on hydrogels. Different intensities of green fluorescence cells. As a result, GADQ1.5% was the potential hydrogel
indicate the location and number of cells, as shown material with good biocompatibility.
in Figure 7a–c. With the increase of culture days, we
observed that the cells adhered onto and proliferated well 4. Conclusion
on the pores of the four hydrogels using calcein-AM and In this work, the substitution degree of 63.31% QCS was
Hoechst stainings. In these four hydrogels, the growth rate synthesized, then Gel, SA, and QCS were configured to
of fibroblasts on GADQ0% was the fastest. After cultured the inks with good rheology, and finally, the 3D hydrogels
for 7 days as shown in Figure 7c, the cells proliferated and with good biocompatibility were fabricated using 3D
distributed on the outer and inner surface of the GADQ printing. Among the GADQ hydrogels with different
hydrogels, and the density of cells on hydrogels at day 7 mass fractions of QCS, GADQ1.5% has the best tensile
significantly increased when compared to days 1 and 4.
properties, appropriate swelling ratio, stable antioxidant
Figure 8a shows the SEM images of L929 cells inoculated performance (exceeding 70%), and good biocompatibility.
on four hydrogels on days 1, 4, and 7. Cell clusters began More importantly, it had the best antibacterial activity
to integrate on the hydrogels on day 4. Due to the favorable against E. coli and S. aureus of 91.06 ± 0.44% and 93.17 ±
sites for cell adhesion, synapses were initially formed and 0.62%, respectively. At the same time, GADQ1.5% showed
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 447 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.689