Page 448 - IJB-9-2
P. 448
International Journal of Bioprinting Fabrication of 3D functional hydrogel for wound dressings
property, and biocompatible performance of the resulting
double-crosslinked GADQ hydrogel dressings as potential
medical applications for wound treatment.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
Chitosan (90% degree of deacetylation, and average
molecular weight of 2 × 10 g/mol), gelatin (gel strength
5
240 g Bloom), sodium alginate (viscosity: 200–500 mPa·s),
2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC),
3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-1-ethylcarbodiimide
hydrochloride (EDC), dopamine, and N-hydroxysuccinimide
(NHS) were provided by Adamas-beta® (Shanghai Titan
Scientific Co.). Anhydrous calcium chloride (purity 96%) was
obtained from Shanghai Maclin Biochemical Technology
Co., Ltd.
The L929 fibroblast cell line was supplied from Qingqi
(Shanghai) Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd. Cell
Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) was purchased from Beyotime
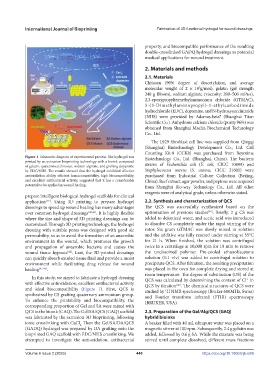
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of experimental process. The hydrogel was Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The bacteria
printed by an extrusion bioprinting technology with a bioink composed
of gelatin, quaternized chitosan, sodium alginate, and grafting dopamine strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli, CICC 10899) and
by EDC/NHS. The results showed that the hydrogel exhibited effective Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus, CICC 21601) were
antioxidation ability, efficient hemocompatibility, high biocompatibility, purchased from Industrial Culture Collection (Beijing,
and excellent antibacterial activity, suggested that it has a considerable China). Beef extract, agar powder, and peptone were acquired
potential to be applied in wound healing. from Shanghai Bio-way Technology Co., Ltd. All other
reagents were of analytical grade, unless otherwise stated.
prepare intelligent biological hydrogel scaffolds for clinical
application . Using 3D printing to prepare hydrogel 2.2. Synthesis and characterization of QCS
[39]
dressings to speed up wound healing has many advantages The QCS was successfully synthesized based on the
[46]
over common hydrogel dressings [40,41] . It is highly flexible optimization of previous studies . Briefly, 2 g CS was
where the size and shape of 3D printing dressings can be added to deionized water, and acetic acid was introduced
customized. Through 3D printing technology, the hydrogel to dissolve CS completely under the rapid stirring of the
dressing with suitable pores was designed with good air rotor. Six gram GTMAC was slowly mixed in solution
permeability, so as to avoid the formation of an anaerobic and the additive was fully reacted under stirring at 55°C
environment in the wound, which promotes the growth for 21 h. When finished, the solution was centrifuged
and propagation of anaerobic bacteria and causes the twice in a centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min to remove
wound tissue hypoxia . Last, the 3D-printed dressings the undissolved polymer. Pre-cooled ethanol/acetone
[42]
can quickly absorb exuded tissue fluid and provide a moist solution (1:1 v/v) was added to centrifugal solution to
environment while facilitating drug release for wound precipitate QCS. After filtration, the resulting precipitation
healing [43-45] . was placed in the oven for complete drying and stored at
room temperature. The degree of substitution (DS) of the
In this study, we aimed to fabricate a hydrogel dressing -1
with effective antioxidation, excellent antibacterial activity QCS was calculated by determining the content of Cl in
[46]
QCS by titration . The chemical structures of QCS were
and ideal biocompatibility (Figure 1). First, QCS is studied by H NMR spectroscopy (Bruker 600MHz, Swiss)
1
synthesized by CS grafting quaternary ammonium group. and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
To enhance the printability and biocompatibility, the (BRUKER, USA).
corresponding proportion of Gel and SA were mixed with
QCS in the bioink (GAQ). The Gel/SA/QCS (GAQ) scaffold 2.3. Preparation of the Gel/Alg/QCS (GAQ)
was fabricated by the extrusion 3D bioprinting, following hybrid bioinks
ionic crosslinking with CaCl Then the Gel/SA/DA/QCS A beaker filled with 40 mL ultrapure water was placed on a
2.
(GADQ) hydrogel was prepared by DA grafting onto the magnetic stirrer at 100 rpm. Subsequently, 2.4 g gelatin was
bioprinted GAQ scaffold with EDC/NHS crosslinking. We added, followed by 0.6 g SA. While the mixture was being
attempted to investigate the antioxidation, antibacterial stirred until complete dissolved, different mass fractions
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 440 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.689