Page 39 - IJB-9-3
P. 39
International Journal of Bioprinting Comparison of different 3D printing technologies
c
A − A c
C = t a •100% (I)
f
A t c
Where A is the total area and y A is the area generated
c
c
a
t
after depositing the filament.
Figures 5 and 6 show an example of how the test is
carried out and a sample of how it would look, respectively.
If the filament does not collapse, coinciding the real area
and the total area, the collapse coefficient is 0%. Table 2
shows the results of the test.
For this study, and based on the results of the sessile
drop method shown in Table 1, 10% GelMA and ColMA
with a target concentration of 5 mg/mL were discarded, as
they were not within the 35°–80° range of the sessile drop
method.
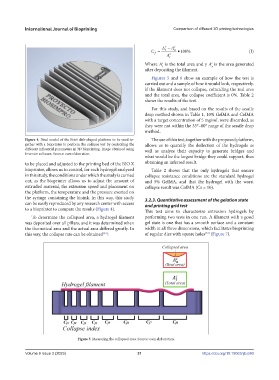
Figure 4. Final model of the Petri dish-shaped platform to be used to- The use of this test, together with the proposed platform,
gether with a bioprinter to perform the collapse test by controlling the allows us to quantify the deflection of the hydrogels as
different influential parameters in 3D bioprinting. Image obtained using well as analyze their capacity to generate bridges and
Inventor software. Source: own elaboration.
what would be the largest bridge they could support, thus
to be placed and adjusted to the printing bed of the BIO X obtaining an inferred result.
bioprinter, allows us to control, for each hydrogel analyzed Table 2 shows that the only hydrogels that ensure
in this study, the conditions under which the study is carried collapse resistance conditions are the standard hydrogel
out, as the bioprinter allows us to adjust the amount of and 5% GelMA, and that the hydrogel with the worst
extruded material, the extrusion speed and placement on collapse result was ColMA (Cs = 10).
the platform, the temperature and the pressure exerted on
the syringe containing the bioink. In this way, this study 3.2.3. Quantitative assessment of the gelation state
can be easily reproduced by any research center with access and printing grid test
to a bioprinter to compare the results (Figure 4).
This test aims to characterize extrusion hydrogels by
To determine the collapsed area, a hydrogel filament performing two tests in one run. A filament with a good
was deposited over all pillars, and it was determined when gel state is one that has a smooth surface and a constant
the theoretical area and the actual area differed greatly. In width in all three dimensions, which facilitates bioprinting
[34]
this way, the collapse rate can be obtained : of regular dies with square holes (Figure 7).
[33]
Figure 5. Measuring the collapsed area. Source: own elaboration.
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 31 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.680