Page 207 - IJB-9-4
P. 207
International Journal of Bioprinting b-Ti21S TPMS FGPs produced by laser powder bed fusion
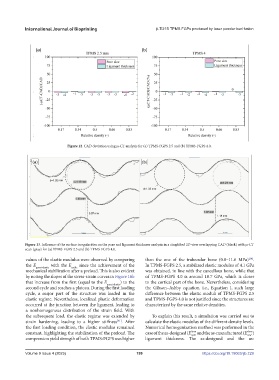
Figure 12. CAD deviation using m-CT analysis for (a) TPMS-FGPS 2.5 and (b) TPMS-FGPS 4.0.
Figure 13. Influence of the surface irregularities on the pore and ligament thickness analysis in a simplified 2D view overlapping CAD (black) with m-CT
scan (gray) for (a) TPMS-FGPS 2.5 and (b) TPMS-FGPS 4.0.
values of the elastic modulus were observed by comparing than the one of the trabecular bone (0.8–11.6 MPa) .
[34]
the E quasi-elastic with the E cyclic since the achievement of the In TPMS-FGPS 2.5, a stabilized elastic modulus of 4.1 GPa
mechanical stabilization after a preload. This is also evident was obtained, in line with the cancellous bone, while that
by noting the slopes of the stress-strain curves in Figure 16b of TPMS-FGPS 4.0 is around 10.7 GPa, which is closer
that increase from the first (equal to the E quasi-elastic ) to the to the cortical part of the bone. Nevertheless, considering
second cycle and reaches a plateau. During the first loading the Gibson–Ashby equation, i.e., Equation I, such large
cycle, a major part of the structure was loaded in the difference between the elastic moduli of TPMS-FGPS 2.5
elastic regime. Nevertheless, localized plastic deformation and TPMS-FGPS 4.0 is not justified since the structures are
occurred at the junction between the ligament, leading to characterized by the same relative densities.
a nonhomogenous distribution of the strain field. With
the subsequent load, the elastic regime was extended by To explain this result, a simulation was carried out to
strain hardening, leading to a higher stiffness . After calculate the elastic modulus of the different density levels.
[61]
the first loading condition, the elastic modulus remained Numerical homogenization method was performed in the
constant, highlighting the stabilization of the preload. The case of the as-designed (E hom and the as-manufactured (E hom )
real
nom
compression yield strength of both TPMS-FGPS was higher ligament thickness. The as-designed and the as-
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 199 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.729