Page 429 - IJB-9-4
P. 429
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of artificial blood vessel
A
B
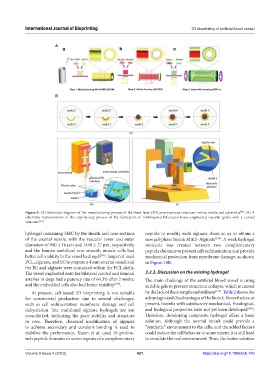
Figure 9. (A) Schematic diagram of the manufacturing process of the three-layer (3D) arteriovenous structure: intima media and adventitia . (B) A
[66]
schematic representation of the step-by-step process of the fabrication of multilayered bifurcated tissue-engineered vascular grafts with a curved
structure [165] .
hydrogel containing SMC by the sheath and core sections peptide to modify each alginate chain so as to obtain a
of the coaxial nozzle, with the vascular inner and outer new gel-phase bioink Mitch-Alginate [178] . A weak hydrogel
diameters of 990 ± 16 μm and 1449 ± 27 μm, respectively, molecule was created between two complementary
and the human umbilical vein smooth muscle cells had peptide domains to prevent cell sedimentation and provide
better cell viability in the vessel hydrogel [176] . Jang et al. used mechanical protection from membrane damage, as shown
PCL, alginate, and EC to prepare a 4 mm arterial vessel, and in Figure 10B.
the EC and alginate were contained within the PCL shells.
The vessel implanted onto the bilateral carotid and femoral 3.2.3. Discussion on the existing hydrogel
arteries in dogs had a patency rate of 64.3% after 2 weeks, The main challenge of the artificial blood vessel is using
and the embedded cells also had better viability [177] . suitable gels to prevent structural collapse, which is caused
At present, cell-based 3D bioprinting is not suitable by the lack of the strength and stiffness [179] . Table 2 shows the
for commercial production due to several challenges, advantages and disadvantages of the bioink. Nevertheless, at
such as cell sedimentation membrane damage and cell present, bioinks with satisfactory mechanical, rheological,
dehydration. The traditional alginate hydrogels are ion and biological properties have not yet been developed [180] .
cross-linked, indicating the poor stability and structure Therefore, developing composite hydrogel offers a basic
in vivo. Therefore, chemical modification of alginate solution. Although the normal bioink could provide a
to achieve secondary and covalent bonding is used to “synthetic” environment to the cells, and the added factors
stabilize the performance. Karen et al. used 10 proline- could induce the cell behavior to some extent, it is still hard
rich peptide domains or seven repeats of a complementary to simulate the real environment. Thus, the better solution
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 421 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.740